An intransitive verb is a verb whose context does not entail a direct object. Having the lack of transitive distinguishes an intransitive verb from the other verb forms that refer to direct objects. This can be a confusing verb form. Although, is used commonly. Words like “pose, look, live, run, rush, sail, scream, read” are all intransitive verbs.
What are Intransitive verbs?
In grammatical terms, a transitive verb is a verb that takes an object, whereas an intransitive verb is a verb that does not take an object.
Intransitive verbs are distinguished from transitive verbs, which take one or more objects, by the absence of transitivity in intransitive verbs. In addition, intransitive verbs are often placed in a category that is distinct from both modal verbs and defective verbs.
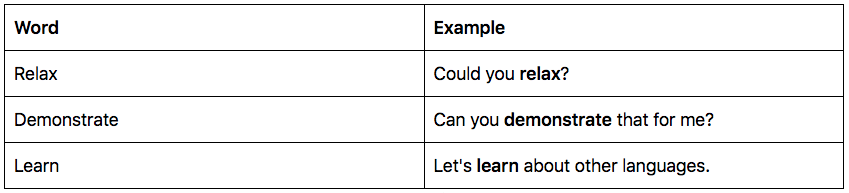
| Word | Example |
| Relax | Could you relax? |
| Demonstrate | Can you demonstrate that for me? |
| Learn | Let’s learn about other languages. |
How Can You Tell If a Verb Is Transitive or Intransitive in a Sentence?
Finding an intransitive verb in a phrase needs you to search for elements that aren’t present in the expression.
Discovering the action verb in the phrase is the first step. When you are first becoming used to distinguish the components of sentences, you may find it helpful to circle or highlight the verb.
After that, look at the information that comes after the verb. Is there a noun in the vicinity that is acting as the recipient of the action?
This noun serves as the immediate object of the sentence. In most cases, it comes just after the verb, however in other cases, a determiner or adjective may come before it.
The verb you discovered is an intransitive verb if it does not have a direct object associated with it.
The following are some examples that might assist you in determining whether or not a verb is intransitive:
- The plants grow quickly in only few months.
- James threw the ball at Sarah’s head.
“grow” is the action verb that should be used in the first sentence. After the verb, there is an adverb, which is “soon,” and then there is a prepositional phrase (in only few months).
There is not a direct object that is being grown upon by the verb “grow.” As a result, the word “grow” is an example of an intransitive verb.
The verb “throw” is used as the action verb in the second sentence. The noun “the ball” comes right after the verb in this sentence. The word “ball” is a noun, while the word “the” is the determining article.
The ball is in the process of being tossed. It is taking in the activity at this time. The word “boy” is the direct object since it is the one that is getting action, hence the word “threw” is a transitive verb.
Difference between transitive verbs
A verb is said to be transitive if it needs an object to convey a complete thinking, while an intransitive verb does not need an object to express a complete concept.
A verb is said to be transitive if it is only meaningful when the action it performs is carried out on an object. An intransitive verb does not require a direct object to make meaning. There are several verbs that may be used in either direction.
People frequently think of transportation when they hear the word “transitive.”
This leads to the erroneous notion that the terms “transitive” and “intransitive” are just more elegant methods of defining “activity” and “nonaction,” respectively.
However, neither of these concepts have any relevance to the question of whether a verb is active or not. Transfer is a better term to relate with the concept of transitive.
A transitive verb must be able to “pass on” its action to another item or person, often known as a “object.” In its most basic sense, “to effect something else” is what “transitive” means.
Difference between irregular verbs
An irregular verb is a verb that does not adhere to the standard conjugation pattern for the simple past and the past participle forms. An irregular verb can also be referred to as an irrational verb.
When forming the past tense and the past participle, regular verbs adhere to the usual grammatical rules of contemporary English by adding “-ed” or “-d” to the end of the verb. When functioning as the primary verb in a phrase, however, irregular verbs replace their many verb forms with terms that are wholly unique to themselves.
Verbs that don’t take a direct object are called intransitive, and they’re the opposite of transitive verbs.
It’s possible for irregular verbs to function as intransitive verbs. It is dependent on the context to determine if a particular verb is transitive or intransitive. This means whether or not it is an action verb, a stative verb, or a linking verb.
How do irregular verbs fit into the category of intransitive verbs?
Run is an irregular verb.
Run – Ran – Run
- The chicken ran.
This sentence contains several irregular verbs, each of which is an example of an intransitive verb since it does not call for an object to be considered complete. The clause has all the necessary elements by itself.
One further illustration of this is the verb sing. Again, it is an irregular form of the verb.
Sing – Sang – Sung
- The singer sung.
Once more, the meaning of this line may stand on its own. This indicates that there is no object need for it. As a result, it is an example of an intransitive verb.

Difference between regular verbs
A verb is said to be regular if it follows the standard pattern for creating the simple past tense as well as the past participle of the verb.
To generate the past forms of a verb in English, the “normal” rule is to add “-ed” or “-d” to the form of the verb that serves as the basis.
Regular verbs, much like irregular verbs, have the potential to function as intransitive verbs as well. This indicates that it is possible to employ these verbs in place of a direct object in the sentence in order to make the statement full.
The following is a list of instances of regular verbs:
1. bark
bark – barked – barked
2. panic
panic – panicked – panicked
3. chirp
chirp – chirped – chirped
4. walk
walk – walked – walked
5. open
open- opened – opened
Now, let’s have a look at how these common verbs may also function as intransitive verbs:
1. The dog barked.
2. the thief panicked.
3. The baby birds chirped.
4. The old lady walked.
5. The door opened.
Verbs are the key to completing each of these phrases, which would not be possible without them. Because of this, the verbs that are considered regular in these phrases are also considered intransitive verbs.
Difference with phrasal verbs
A verb composed of two or more words is referred to as a phrasal verb. In most cases, a verb is accompanied by an adverb and/or a preposition in these terms.
Phrasal verbs are challenging because their meanings are frequently very unlike the original meaning of the verb they are based on.
For instance, the meaning of the phrasal verb “to take over” is “to get command over something.”
- Mr. Charles has taken over.
Every verb can be either transitive or intransitive, depending on the context. A transitive verb is one that takes an object to complete its meaning. Take, for instance:
- Study French.
- Throw the boomerang.
In the case of intransitive verbs, the absence of an object is not required. Take, for instance:
- Run to the church.
- Come on time.
- Go to the pharmacy.
Because no object has to be considered, it is simpler to utilize intransitive phrasal verbs. The following are some instances of phrasal verbs that do not include an object:
- Why don’t you move over?
- His grandfather passed on.
- My sister and I get on really well.
- The tickets sold out.
What does “taking a direct object” mean?
A noun that is the recipient of the action of the verb is referred to as the “direct object.” In most cases, direct objects provide responses to the queries “what?” and “whom?”
There are several verbs that do not require a direct object. Some verbs do not need a direct object since it does not make sense. Consider the example of laughing. You are not allowed to chuckle at something.
Verbs that require an accompanying direct object are referred to as transitive verbs, whereas verbs that do not require an object are known as intransitive verbs.
Examples of intransitive verbs
- The seed grew.
- The cat disappeared.
- Charles lied.
- His new shop opened.
- James and Charles talked.
- The choir group sang.
- My mother listens.
- Brad’s phone rang.
- His mother coughed.
Examples of verbs that are both transitive and intransitive
Here are examples of verbs that are both transitive and intransitive:
1. James walked.
- James walked his pet.
2. Emma and Daniel drive.
- Emma and Daniel drive a Mercedes.
3. Jennifer reads.
- Jennifer reads one book a day.
4. Jose understands.
- Jose understands what you mean.
Common intransitive verbs list
Here are common intransitive verbs.
Words with examples
1. Rain
- It was raining.
2. Sing
- Justin was singing.
3. Run
- The racers run.
4. Die
- His grandfather died.
5. Sleep
- Sleeping Beauty slept.
Intransitive verbs with no passive form
Using the passive voice for such statements is impossible since they contain intransitive verbs.
This is due to the absence of an object in the phrases in question. Using the passive voice for a sentence is impossible if the statement does not contain an object.
Take, for instance:
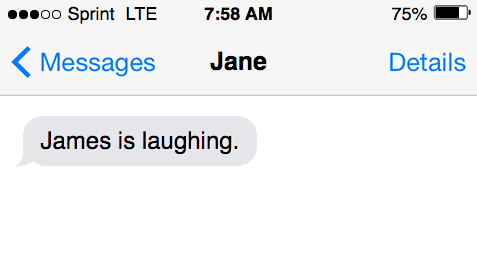
- James is laughing.
- Her grandmother is gone.
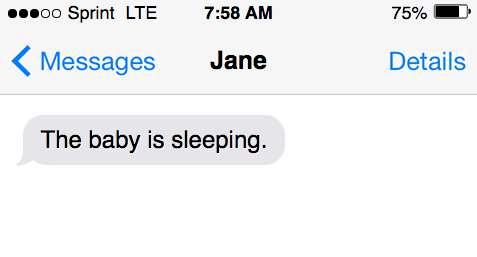
- The baby is sleeping.
- The puppy is crying.
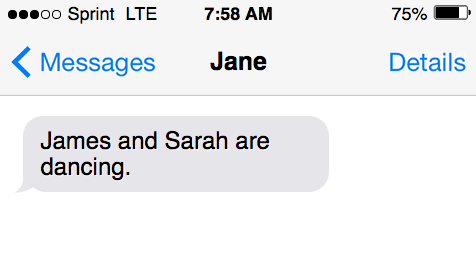
- James and Sarah are dancing.
- Brad was standing.
FAQs
What’s the difference between transitive and intransitive verbs?
The difference between lies in the necessity of a direct object. The intransitive verb does not take a direct object, whereas the transitive verb does take a direct object. Many common verbs can be both direct and indirect objects.
How do intransitive verbs and a prepositional phrase work together?
Intransitive verbs can be used in the passive voice when the prepositional is included, as in, “The homes were lived in by millions of people.” In this sentence, we can see that prepositional phrases are getting used to help describe a complete sentence.
Can action verbs, stative verbs, and linking verbs be intransitive verbs?
Yes. It is dependent on how they are used, but it can be.
How does a noun phrase work with intransitive verbs?
Every verbal sentence must have that structure, this contains a singular noun phrase without a preposition, called an unmarked noun phrase.
Sources:
- List of 100+ Intransitive Verbs | Useful Intransitive Verb Examples
- Intransitive Verb Guide: How to Use Intransitive Verbs
- Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
- Intransitive Verbs
- Direct Objects in English (with Examples)
- Intransitive Phrasal Verbs
- Transitive and Intransitive Phrasal Verbs
- Intransitive Phrasal Verbs: Examples & Overview
- What Are Regular Verbs? (with Examples)
- What Are Intransitive Verbs? List And Examples
- Transitive and Intransitive Verbs — What’s the Difference?
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



