Among the many verb tenses, present continuous is one of the most commonly used tenses in English. It is used in daily conversations by people at large. Here is a brief breakdown of the present continuous. The article details the definition, different types of tenses, uses of present continuous tense, the structure of present continuous, and examples.
What Is Present Continuous Tense?
The present continuous, also known as the present progressive tense, refers to actions that are taking place now, these days, or nowadays. Here, the action hasn’t been completed yet. It is continuing and will do so for a little while.

For example: She is cleaning the house. Here, the person is cleaning the house right now and will continue to do so for a while. The action hasn’t ended yet.
Another example: The dog is barking at the birds. Here the action (barking) is taking place right now. In other words, it is a temporary action that will end soon.
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
| I am going. | I am not going. | Am I going? |
| You are going. | You aren’t going. | Are you going? |
| He is going. | He isn’t going. | Is he going? |
| We are going. | We aren’t going. | Are we going? |
What are the other tenses?
In English, there are three basic tenses. Each tense is further divided into four tenses. In total, the list comes to twelve verb tenses, and present continuous is one among them. Here is a full list of all the twelve tenses.
- The Simple Present
- The Present Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Present Perfect
- The Present Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense
- Simple Past
- The Past Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Past Perfect
- The Past Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Simple Future
- The Future Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Future Perfect
- The Future Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense
The table below explains each of these tenses with examples:
| Tense | Function | Rule | Example |
| Present simple | Helps to describe habits, facts, actions, and truth that are not affected by time | Ist form of verb + s/es | He loves pizza. |
| Past simple | Helps to describe events that have happened in the past | IInd form of the verb | She wore a beautiful dress for the party. |
| Future simple | Helps to describe events that will happen in the future | Will/ shall + Ist form | He will go to New York tomorrow. |
| Present perfect | Helps to describe the relevance of past events in the present moment | Has/ have + IIIrd form of the verb | I have learned to ride a bike. |
| Past perfect | Helps to describe events that happened prior to other events in the past | Had + IIIrd form of the verb | She had finished the paper before leaving the hall. |
| Future perfect | Helps to describe events that will be completed between now and a specific point in the future | Will/ have + IIIrd form of the verb | She will have finished the book by tomorrow. |
| Present continuous | Helps to describe ongoing actions | Is/ am/ are + Ist form + ing | “She is reading a book. |
| Past continuous | Helps to describe ongoing events of the past, mostly in relation to another event | Was/ were + Ist form + ing | He was driving to work when the accident happened. |
| Future continuous | Helps to describe future events that will/are expected to continue for a period of time | Will be + Ist form + ing | I will be going to meet my grandparents tomorrow. |
| Present perfect continuous | Helps to describe events that started in the past and will continue into the present | Has/ have been + Ist form + ing | She has been writing a book for the past one year. |
| Past perfect continuous | Helps to describe events that began, continued, and ended in the past | Had been + Ist form + ing | I had been working in this company for ten years when I got the promotion. |
| Future perfect continuous | Helps to describe events that began in the past but will continue until a point in the future | Will/ shall have been + Ist form + ing | I will have been doing business with her for one year. |
While these are all different types of tenses, the present simple, the past simple and the present perfect are the most commonly used.
Watch a short video lesson
How Is Present Continuous Different From Other Tenses?
Among many differences, the significant difference between the present continuous and other tenses is the structure. To understand them in detail, below is a comparison between present continuous with tenses like simple present and present perfect continuous.
Present Continuous vs. Simple Present
- The simple tense is used when talking about actions that are done consistently. In other words, it is used when performing things that are done routinely. For example: He plays football. In the sentence “He plays football,” the person plays football as a part of his daily life. It is not temporary instead it is a permanent routine.
On the other hand, present continuous talks about actions that are happening now and will end in a little while. For example: She is eating now. Here, the “eating” action is happening now. It is temporary and will soon end.
- In comparison to the simple present, forming a present continuous sentence is difficult. The structure of the present continuous is – subject + am/is/are + present participle (-ing).
On the other hand, the structure of the simple present is – subject + Verb1 + object.
- The most common time frame words used in the simple present are always, often, generally, every day, every week, sometimes, and never.
In comparison, the common time frame words used in the present continuous are now, still, right now, these days, and at the moment.
- All verbs are used in the simple present tense, whereas some verbs cannot be used in present continuous. Dynamic verbs are used, but stative verbs are not used in present continuous.
Present Continuous vs. Present Perfect Continuous
- In the present continuous, the action is happening now. For example: I am eating now. Here the action of “eating” is taking place now.
In comparison, the present perfect continuous indicates that the action has started in the past and is continuing in the present. For example: She has been learning Ballet since 2020. Here the person started learning ballet in 2020 and still continuing with it.
- The present continuous structure is – subject + am/is/are + present participle (-ing). On the other hand, the structure of present perfect continuous is – subject + have/has + been + present participle(ing).

How to Use Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous is used in many situations. It is used when:
- Talking about things that are taking place now.
- Describing an action that is in progress but takes a longer time to perform.
- Describing an action that will happen in the near future.
- Describing a repetitive, irritating action.
Action Taking Place Now
The tense is used when talking about an action that is happening now. The sentences have words like now, right now, and at the moment which indicates the action is taking place now.
| Positive statement word | Example |
| I | eat |
| You | eat |
| She | eats |
| It | eats |
Examples:
- I am listening to music right now.
- They are dancing at the party now.
Longer Actions In Progress
The present continuous is used to describe actions that are happening now but will take a longer time period to finish.
Examples:
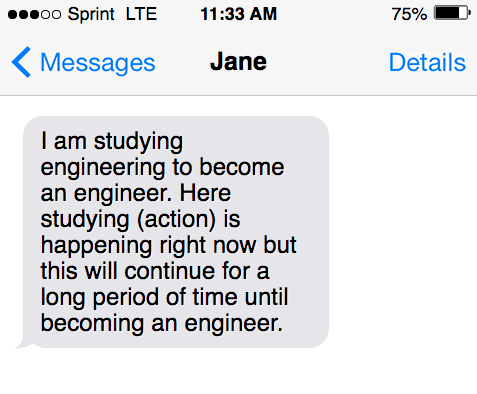
- I am studying engineering to become an engineer. Here studying (action) is happening right now but this will continue for a long period of time until becoming an engineer.
- I am practicing singing to become a classical singer.
Near Future
It is used to describe events that are planned for the near future. The sentences have a “future word” in them. Words like tomorrow and next week are used.
Examples:
- She is visiting the theatre tomorrow. Here, the person has planned to visit the theatre but will do it in the future which is tomorrow.
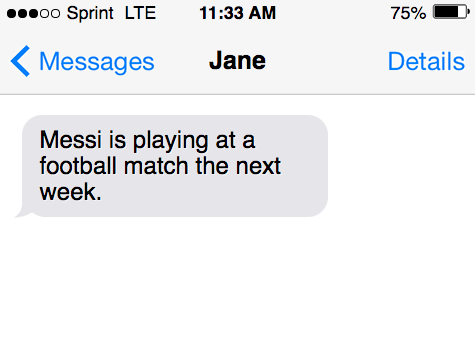
- Messi is playing at a football match the next week.
Repetition
The tense is used to describe events that repeat and irritate.
Examples:
- She is always complaining about her workplace. Here, the person is repeatedly complaining about her workplace.
- He is constantly coughing. I wish he takes some medicine.
Present Continuous Grammar Rules
- The present continuous is formed with the auxiliary verb and the present participle of the verb. The auxiliary verb comes in the form of am/is/are.
- At the end of the present particle of the verb, an “ing” is added. Here is the structure: subject + am/is/are + present participle (-ing).
- It is created using affirmative sentences as well as negative sentences.
- For negative sentences, there is a slight difference in the structure. The structure is – subject + am/is/are + not + present participle (-ing).
- It is also used in creating questions. But, when creating questions, there is a slight difference. The auxiliary verb and subject interchange their positions. The structure is – am/is/are + subject + present participle (ing).
Examples of Present Continuous
Here are examples of present continuous.
Affirmative Sentences
- He is riding a horse.
- She is swimming in the lake.
Negative Sentences
- I am not inviting her to my house. (I (subject) + am (auxiliary verb) + not (negative) + inviting (present participle with “ing”)).
- She is not eating an apple. (She (subject) + is (auxiliary verb) + not (negative) + eating (present participle with “ing”)).
Questions
- Is she laughing at me? (Is (auxiliary verb) + she (subject) + laughing (present participle with “ing”)).
- Am I irritating you with my questions? (Am (auxiliary verb) + I (subject) + irritating (present participle with “ing”)).
- Why is he staring at me? (Is (auxiliary verb) + he (subject) + staring (present participle with “ing”)).

Sources
- Learning the English Present Continuous Tense?
- Present Simple Vs Present Progressive Tense Difference
- Difference Between Present Simple and Present Continuous
- Present Simple and Present Continuous | Learn English
- Present Continuous Tense (Present Progressive Tense)
- Present Continuous | Grammar | EnglishClub
- Present continuous | English grammar
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



