What is a homonym? Is it exactly like a homophone? How are they different? Or are they different at all? These are all great questions that will get answered in this complete guide about homonyms. Continue reading to learn more.
What is a Homonym?
A homonym refers to words that have the same spelling, and the exact same pronunciation, but differ in the meaning they convey. In such cases, it is impossible to understand what one is trying to convey without the context.

Definition
According to Merriam-Webster, a homonym is “one of two or more words spelled and pronounced alike but different in meaning”
It is derived from the Greek word ‘Homonymos,’ which means “having the same name.”
For example, consider the word ‘bat.’
Bat – It has two different meanings
- A mammal that can see in the dark.
- A piece of wood is cut in a specific way and used in the game of baseball, cricket or table tennis to hit the ball.
Similarly, the word ‘address‘ has 2 different meanings depending on context.
- The location of a place is its address.
- To talk to a person or a group of people.
Understanding Homonym vs. Homophone
Homonyms are words that have the same spelling and the precisely same pronunciation but differ in the meaning they convey. Homophones are words with the same pronunciation but differ in spelling and the meaning they convey.
Homophones are a kind of homonym.
Let’s now look at a few examples of homophones:
- Aural and Oral
- Quire and Choir
- Ascent and Assent
- Dual and Duel
- Hour and Our
- Beat and Beet
- Fined and Find
- Disburse and Disperse
- Band and Banned
- Eve and Eave
- Gait and Gate
- Break and Brake
- Here and Hear
- Islet and Eyelet

Examples of homophones (meaning and use)
Advice and Advise
Advice – Get advice from an expert before you invest in the stock market.
Advise – The captain was strongly advised by the doctor to take rest and not play the next game.
Weather and Whether
Weather – Wear suitable clothes during cold weather or you will fall sick.
Whether – I asked Paul whether he had any intentions of joining us in community service.
Baron and Barren
Baron – Gina’s elder brother is a media baron.
Barren – The local community has worked tirelessly to transform the barren land into a tourist site.
Dual and Duel
Dual – Louis De Broglie suggested the idea of wave-particle duality.
Duel – Hector had no other option but to agree to the duel.
Hew and Hue
Hew – The dwellers of the Silent Valley took hours to sharpen the axe before hewing the log.
Hue – When white light passes through droplets of water, it splits into seven different hues, which is what we call a rainbow.
Bolder and Boulder
Bolder – Her continuous intrusion into Delta dynamics, coupled with little resistance from the team, made Asha even bolder.
Boulder – Even though Bryan was explicitly instructed to keep in mind the boulders on the slope, he paid no heed much to his peril.
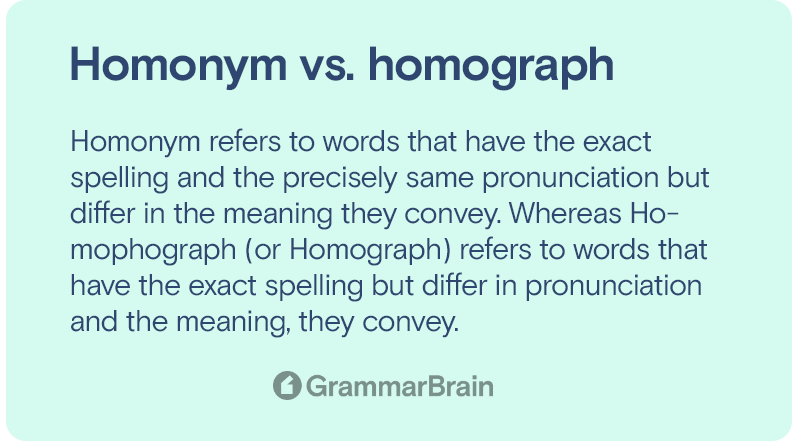
Homograph vs Homonym
Homonym refers to words that have the exact spelling and the precisely same pronunciation but differ in the meaning they convey. Whereas Homophograph (or Homograph) refers to words that have the exact spelling but differ in pronunciation and the meaning, they convey.
Consider a few examples of homographs:
Lead –
Meaning 1: a metal
Meaning 2: being ahead in a competition
Minute –
Meaning 1: sixty seconds
Meaning 2: something very small
Bank –
Meaning 1: an institution that deals with financial transactions
Meaning 2: the piece of land at the horizontal edges of a river
Close –
Meaning 1: to shut
Meaning 2: to be near someone or something
Letter –
Meaning 1: the alphabet
Meaning 2: a piece of paper containing some kind of a message
Bow –
Meaning 1: to bend your upper body in respect
Meaning 2: a curved piece of wood whose ends are tied up together by a string.
Firm –
Meaning 1: an organization/ company
Meaning 2: the quality of being rigid, not changing its shape under an applied force
Fan –
Meaning 1: a person who respects and supports another person
Meaning 2: an electronic appliance
Class –
Meaning 1: different grades in school
Meaning 2: being elegant or stylish in appearance or behavior
Does –
Meaning 1: a group of female deer
Meaning 2: the present form of the verb ‘do’
Examples of Homograph (with their meanings)
Date
Dates are good for health. But you should consume them within limits.
It is not an easy task to remember the dates of important events in history. The Internet has largely obviated the need to.
Attribute
One of Timothy’s finest attributes is his liveliness, the prime reason behind his meteoric rise.
As a mark of respect, the captain of the host team attributed the victory to the oldest player in the team, who was going to retire.
Coordinates
As soon as the spy got the coordinates of the hideouts, he immediately drove down to the head office.
It was thanks mainly to the improved coordination of various departments that the takeover bid was solved quickly and efficiently.
Proceeds
Don’t proceed any further unless you have understood and practiced the previous concepts thoroughly.
The net proceeds of the company were likely to break all the previous records and reach an all-time high.
Refuse
The new recruit refused to take any bribe, just as the bosses had expected.
No refuse must be littered on the roads or beaches; every speck on the street is a potential threat to our blue flag certificate.
Compound
It took years of patience and dedicated hard work by the researchers to find the right amount of chemicals to form the compound, which would prove to be a life-saving one.
Being the senior police official, Ramon decided to calm the crowd and promised them immediate legal action to not compound the problem.
Understanding the difference between Synonym, Antonym, and Homonym
- Synonyms – Two words having similar or the same meanings. For example – Terrible and Horrible.
- Antonyms – Two words that mean the exact opposite. For example – Front and Back.
- Homonyms – Words that convey a different meaning but have the same sound and spelling. For example – Kind (Generous, or a type)
Understanding the difference between a Paronym and Homonym
Paronym – Paronyms are those words whose phonemic representations are similar. They are derived from the same root word.
Example – Adjacent and Adjoining.
Examples
1. Adjacent and Adjoining
He was waiting for his turn in an adjacent room.
The thieves were hiding in the adjoining room when the police rushed in.
2. Wrest and rest
Wrest – The momentum was wrestled back by the Islanders after remaining behind for most of the initial hour of the game.
Rest – Saul was advised by the doctors to take adequate rest in order to heal faster.
Homonym examples
Let’s now take a look at some examples of Homonyms.
- Theirs and There’s
- It’s and Its
- Won and One
- Accede and Exceed
- Plane and Plain
- Fare and Fair
- Who’s and Whose
- Blue and Blew
- New and Knew
- No and Know
More examples of Homonyms
Break and Brake
Break – Everyone in the class played soccer or cricket for half an hour during the lunch break.
Brake – Had Jessie not pulled the brakes in time, the child would have been seriously injured.
Chilli and Chile
Chilli – Chilli and other spices are often used to make food more delicious.
Chile – Chile is not just a beautiful country. It is surprisingly affordable as well.
Clime and Climb
Clime – The clime of these islands is continuously changing for the worse due to changes in atmospheric processes brought about by humans.
Climb – Climbing a rope is hard, but nothing that a pair of solid forearms could not accomplish.
Band
The band practiced a lot before their performance, which helped them improvise when the tuning went off on D-day.
Alyssa tied her hair up in a ponytail with the help of a band she found in her make-up kit.
FAQs
What is the difference between homonyms, homophones, and homographs?
- Homonym – Same spelling and sound, but different meaning
- Homophone – Same sound, but different spelling and meaning.
- Homograph – Same spelling, but different sound and meaning.
What are examples of homonyms?
- I and Eye
- Ate and Eight
- Plain and plane
- Ear and Year
Is every Homophone a kind of Homonym?
Yes.
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



