What are antonyms? How does an antonym work? How do I form an antonym? Antonyms can help you enhance your English. They help to create distinctions between words, phrases, and general expressions. In this article, we’re going to cover what antonyms are, how they are used, and how to use them in your general English (and writing).

What is an antonym?
An antonym is a term that has the inverse meaning of that other word. Cold and hot, for example, are antonyms, as are evil and good. Antonyms can be any word, including nouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, and prepositions.
Definition of Antonym
Antonym derives from the word antonymy, a precise grammar term describing words with conflicting meanings. Words with opposing meanings are known as antonyms. An antonym of night, for example, is the day, while an antonym of off is on.
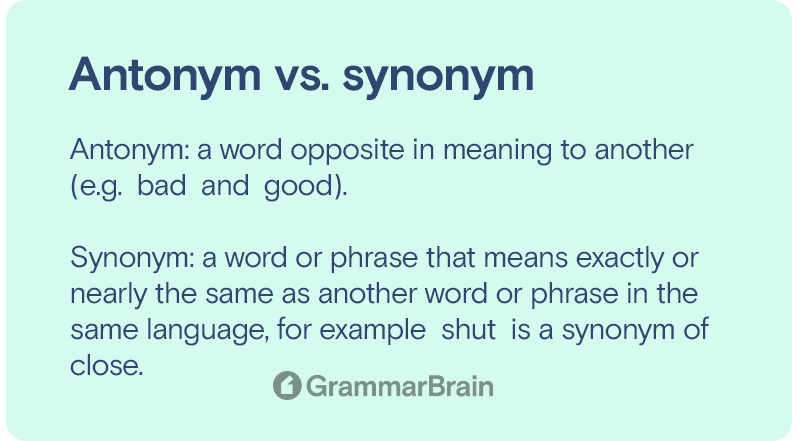
| Antonym (Definition) | Synonym (Definition) |
| a word opposite in meaning to another (e.g. bad and good). | a word or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word or phrase in the same language, for example shut is a synonym of close. |
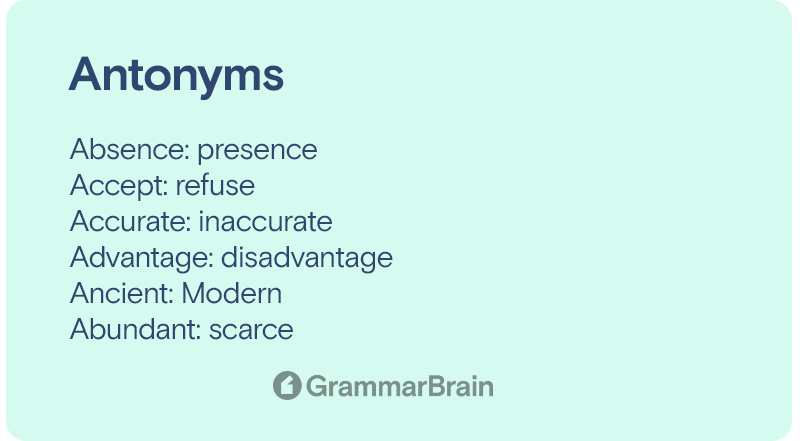
Some words with their antonyms
- Absence: presence
- Accept: refuse
- Accurate: inaccurate
- Advantage: disadvantage
- Ancient: Modern
- Abundant: scarce
- Artificial: natural
- Attractive: repulsive
- Borrow: lend
- Bravery: cowardice
- Create: destroy, demolish
- Bold: timid, meek
- Capable: incapable
- Combine: separate
- Conceal: reveal
- Common: rare
- Decrease: increase
- Definite: indefinite
- Despair: hope
- Discourage: encourage
- Employer: employee
- Expand: contract
More antonyms
- Forget: Remember
- Frequent: Seldom
- harmful: Harmless
- horizontal: Vertical
- imitation: Genuine
- inhabited: Uninhabited
- inferior: Superior
- intentional: Accidental
- justice: Injustice
- knowledge: Ignorance
- landlord: Tenant
- likely: Unlikely
- minority: Majority
- miser: Spendthrift
- obedient: Disobedient
- optimist: Pessimist
- permanent: Temporary
- plentiful: Scarce
- private: Public
- prudent: Imprudent
- qualified: Unqualified
- satisfactory: Unsatisfactory
- tame: wild
- vacant: Occupied
Antonym vs. synonym
Antonyms are connected to synonyms, which are words with the same meaning. Synonyms and antonyms have different implications; whereas antonyms are words with opposite meanings, synonyms share the same meaning. Consider the word huge as an example.
Small is the antonym of huge. This is because huge and little are polar opposites.
On the contrary, large is a synonym for big since big and large signify the same thing.
Some words with their synonyms and antonyms
Abate
Synonym: Moderate, decrease
Antonym: Aggravate
Adhere
Synonym: Comply, observe
Antonym: Condemn, disjoin
Abolish
Synonym: Abrogate, annul
Antonym: Setup, establish
Acumen
Synonym: Awareness, brilliance
Antonym: Stupidity, ignorance
Abash
Synonym: Disconcert, rattle
Antonym: Uphold, Discompose
Absolve
Synonym: Pardon, forgive
Antonym: Compel, Accuse
Abjure
Synonym: Forsake, renounce
Antonym: Approve, Sanction
Abject
Synonym: Despicable, servile
Antonym: Commendable, Praiseworthy
Abound
Synonym: Flourish, proliferate
Antonym: Deficient, Destitute

What do antonyms do?
Antonyms make your statements more efficient. Putting contrasting words together, antonyms underline their distinctions and strengthen the single words. You can employ antonyms in three different ways. They are as follows:
Comparisons
Antonyms are excellent for contrasting two distinct items and bringing attention to their distinctions. For instance, when writing an article that compares different topics, employing a couple of antonyms might help you express what distinguishes them.
Assume you’re discussing the differences between living in cities and living in rural locations. Rather than just providing facts about each, employ antonym pairings to express the distinctions more vividly.
So, you may write rural life as “peaceful” and urban life “noisy” or argue that rural regions have “few” people while urban ones have “many.”
Descriptions
The easiest way to express something might be to describe what it isn’t. Using opposite words with a negative can offer additional aspects to your explanations and enhance your choice of words in your writing.
Using the opposites highlights that the individual decides not to appear humble or modest, which imparts a bit more description than just labeling them “arrogant.”
Someone arrogant, for example, can be described as “not humble” or “not modest.” In other words, you’re essentially saying the same thing since humble and modest are antonyms for arrogant.
Remember that positive explanations are generally preferable to negative ones; therefore, opposites words like antonyms are not always appropriate for explanations.
Nonetheless, negative descriptions function as effectively as positive ones. For instance, insects are typically little; therefore, mentioning a “huge insect” accentuates the word.
Antonyms can help you write more persuasively by reinforcing your descriptive words and testing your reader’s expectations.
Antithesis
The literary element of antithesis directs the strength of contrasts by positioning them close to or nearby one another. As previously said, antonyms call to focus on what distinguishes things, making each word appear stronger.
Antithesis goes one step further by combining antonyms. When revising your work, always search for opportunities to employ antithesis.
After landing on the lunar surface, Neil Armstrong’s comment is among the most renowned illustrations of antithesis: “That’s one small step for man, one giant leap for mankind.”
There are two sets of antonyms here: giant and small, as well as leap and step. If Neil’s first comments on the lunar were, “I took a little stride,” his phrase probably would not be nearly as well-known as now.
His comment highlights the opposing notions of “little stride” and “great leap” by combining them in a single line.
What are contronyms and auto-antonyms?
A contronym is a form of antonym, also referred to as an auto-antonym. Contronyms are words with several meanings, some of which are antonyms of one another.
Contronyms are technically antonyms that also act as homophones (words that sound similar but have distinct meanings).
Contronyms can be classified as any of the antonyms listed below.
Dust is one of the most popular contronyms.
Dust can be used as a verb to mean:
- Dust removal (as in cleaning)
- sprinkling with dust (as in putting sugar on food)
Dust, in essence, means both “remove dust” and “add dust.” Because of the difference in definitions, it is a contronym.
Types of antonyms
When we claim antonyms are opposite words, we’re being a little too broad. There are several forms of opposites and various types of antonyms.
Complimentary antonyms
Complementary antonyms (also referred to as contradictory or binary antonyms) are term pairings in which the affirmative use of one implies the negative use of the opposite. In other words, both have an either-or connection: anything may be either one or both at any given moment.
Examples of complementary antonyms:
- Off – on
- Fake – Genuine
- Dead – Alive
Gradable antonyms
Gradable antonyms, also called polar antonyms, are opposing degrees of the same feature. For example, near and far are gradable antonyms since they are opposed in the distance.
However, these characteristics are relative: The mall may be distant from home, but when contrasted to the center of the Pacific Ocean, it is close.
Examples of gradable antonyms:
- hot — chilly
- long — short
- new — old
Relational antonyms
Relational antonyms (also called converse antonyms) perform opposing roles in a reciprocal connection. Teacher and pupil, for example, are relational antonyms, and neither could exist independently of the other, yet their functions are fundamentally different.
Examples of relational antonyms:
- purchase – sell
- left – right
- parent-kid
How do antonyms and prefixes work together (examples)
Antonyms are frequently used with prefixes (in English). These are tiny syllables ranging from one to three letters that link to the start of words to modify their meaning. A few prefixes invert a word’s meaning, transforming it into its antonym.
Remember that only some words can accept one when employing prefixes, so you can’t just throw them anywhere you want.
Here are some examples of typical prefixes being used as antonym pairings. Each of the following prefixes effectively shifts the meaning of a term to its inverse.
dis-
honest — dishonest
appear — disappear
agree — disagree
i-
logical — illogical
legal — illegal
responsible — irresponsible
in-, im-
possible — impossible
decent — indecent
discreet — indiscreet
non-
believer — nonbeliever
binary — nonbinary
linear — nonlinear
mis-
lead — mislead
behave — misbehave
fortune — misfortune
mal-
function — malfunction
nutrition — malnutrition
adaptive — maladaptive
un-
important — unimportant
necessary — unnecessary
likely — unlikely
How do antonyms and suffixes work together (examples)
Antonyms are not as frequently used with suffixes as used with prefixes (in English).
Suffixes are tiny syllables ranging from one to three letters that link to the end of words to modify their meaning. A few suffixes invert a word’s meaning, transforming it into its antonym.
Here are some examples of typical suffixes being used as antonym pairings. The following suffix effectively shifts the meaning of a term to its inverse.
Less-
care: careless
use: useless
hope: hopeless
fear: fearless
pain: painless
FAQs
What exactly are antonyms?
Words having opposing meanings, such as heated and cooled, right and wrong, and cheerful and melancholy, are examples of antonyms. Two words that can be interchanged are also considered to be antonyms.
When should you use antonyms?
Antonyms are considered advantageous in comparisons to highlight the difference between two opposing items. Antonym pairings can better explain their differences by emphasizing these distinctions.
What are the diverse varieties of antonyms?
Complementary antonyms, such as off and on, cannot both be true. Gradable antonyms, such as huge and little, characterize various sizes by displaying opposing proportions of the same characteristic. Relational antonyms, such as students and teachers, depict opposing positions in the same connection.
What does the word antonym mean?
It means a word that has the exact opposite meaning of the word it’s compared to. A direct antonym is the same.
What is a synonym?
Synonyms and antonyms are similar. A synonym is the same word meaning, although an exchange of the base word.
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



