What’s an adverb, and what are some examples of adverbs in the English language? Adverbs refer to an extraordinarily large and complex part of English language. To learn more about how to correctly use adverbs in sentences, keep reading the current article.
What’s an adverb?
The Cambridge Dictionary adverb definition as:
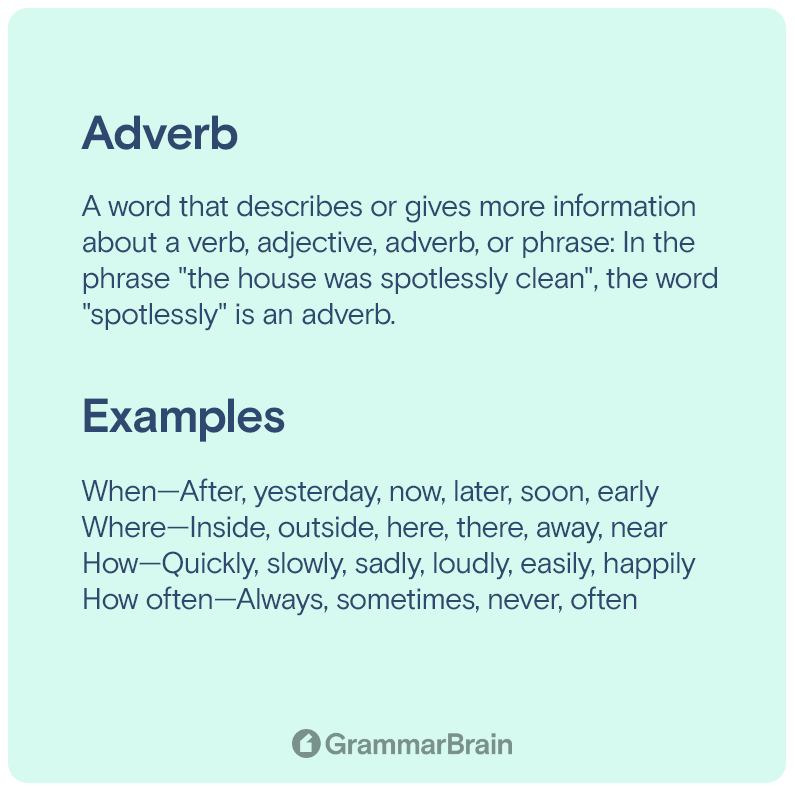
A word that describes or gives more information about a verb, adjective, adverb, or phrase: In the phrase “the house was spotlessly clean”, the word “spotlessly” is an adverb. (Cambridge Dictionary)
Adverbs help modify verbs, other adverbs, and occasionally are used to modify adjectives. Adverbs are descriptive words that provide more information in a sentence about the action or event taking place.
Most likely, you’re familiar with a whole lot of them without even realizing.
See a video lesson
See a few examples of adverbs used in sentences.
See the adverb examples used in the following sentences:
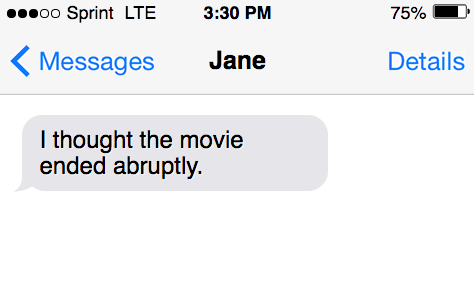
- I thought the movie ended abruptly.
- Her outfit showcased her delightfully quirky personality.
- She lightly dusted the brownies with a layer of powdered sugar before serving.
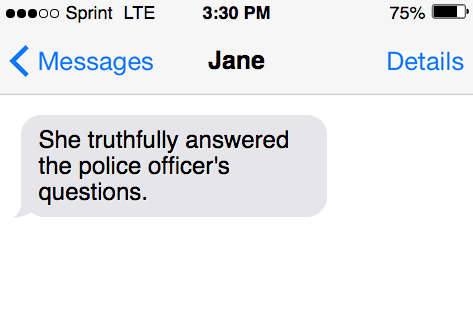
- She truthfully answered the police officer’s questions.
- Quickly finish the grocery shopping so we can get to the party in time.
Adverbs help answer questions: how, when, where, why, or to what extent—how often or how much (e.g., daily, infrequently, etc.) Each of these questions makes up its own category of adverb.
| Reference | Example adverb |
| When | After, yesterday, now, later, soon, early |
| Where | Inside, outside, here, there, away, near |
| How | Quickly, slowly, sadly, loudly, easily, happily |
| How often | Always, sometimes, never, often |
Let’s quickly (see what I did there?) go over the main types of adverbs, for brevity’s sake.
Adverb order
- Adverbs of manner (e.g., She smiled cheerfully.)
- Adverbs of frequency (e.g., We usually go to the cinema on Saturdays.)
- Flat adverbs
- Sentence adverb
- Adverbs of time
- Comparative adverbs/superlative adverbs
Each adverb category name relates to its meaning, the specific information the adverb describes, and the question it answers (i.e., how, when, where, and so forth.)
Before going into each type, remember that adverbs come in two main forms, either as individual words, or as a basic set of words known as an adverbial clause or phrase. More on that to come.

Flat adverbs
In grammar, flat adverbs or simple adverbs take on the same form as corresponding adjective form. These kinds of adverbs do not usually end in the suffix –ly.
The following words that are examples of flat adverbs includes:
- drive slow
- drive fast
- dress smart
- sleep tight
- surf safe
Most flat adverbs can be adapted to the –ly ending like other adverbs. For example, slowly, tightly, quickly, etc.; however, not all simple adverbs can take on the suffix ly at the end of the word.
Words that are flat adverbs that cannot end in ly includes: fast, straight, tough, far, low.
Flat adverbs used to be much more commonly used, and nowadays they are less commonly used in writing.
Some words that end in ly are only adjectives, such as lonely; whereas others, like friendly, can perform as both an adjective and an adverb.
Quick Tip!
The flat adverb has been a source of contention amongst grammarians and writers. Some disagree with its use in writing.
| Phrase | Adverb reference |
| The chef cooked happily. | How a verb was done |
| The chef cooked daily. | How often the verb happened |
| The chef cooked outside. | Where the verb happened |
| The chef cooked yesterday. | When a verb happened |
Adverbs of manner
Adverbs of manner tell us how an action is done, and in what way or manner:
The following sentences are examples of adverbs of manner:
- Beth lightly dusted the brownies with a layer of powdered sugar before serving.
- She truthfully answered the police officer’s questions.
- John plays the flute beautifully.
- He spoke cautiously in front of his in-laws.
- Some elderly people drive slowly.
- Mr. Legree walked slowly to the front of the room and spoke to the children softly but firmly.
- He calmly explained his point of view.
- It rained heavily all through the night.
- My brother drives very fast and aggressively.
- A car suddenly came round the corner and nearly hit us!
- Brenda tearfully said goodbye to her boyfriend.
Most adverbs of manner end with –ly; and this ending makes it easy to identify adverbs of manner in most sentences. Keep in mind, not all words that end with the suffix –ly are adverbs, some are adjectives (like friendly.)
In the sentences above showcasing adverbs of manner, see how the adverb in each sentence answers how something is done; or in what fashion the action of the sentence was done:

In the first sentence, ‘Beth lightly dusted the brownies with a layer of powdered sugar before serving,’ the adverb ‘lightly‘ tells us in what style or way Beth went about doing the action, she layered the powdered sugar lightly. If this sounds like a trivial detail, it’s not.
The fact that Beth layered the powdered sugar lightly says a lot about Beth as a person: she’s the kind of person that takes the time to lightly powder sugar on top of brownies.
Beth could just as easily have layered the sugar hurriedly, quickly, hastily or carelessly; each of which is also an adverb of manner.
Likewise, in the third example, the adverb beautifullyanswers the question, ‘how does John play the flute?’ The second example tells us how she answered the police, truthfully. The fourth example, he spoke cautiously, and so forth.
Simply put, adverbs that fill in the how of a sentence are adverbs of manner, and many adverbs fall under this category.
These details can affect the entire sentences meaning, though they are not necessarily sentence adverbs. That said, this offers a natural segue to a different adverb type—next up.
Sentence adverbial phrases
When an adverb modifies or affects the meaning of entire sentences, they are known as sentence adverbs, sentence adverbials, or disjuncts.
Usually, they are the first word to appear in the sentence, and they emphasize emotion, and the personal attitude/tone of the writer.
Most adverbs end in –ly, and are followed by a comma. Words like ‘fortunately,’ and ‘obviously,’ are examples of sentence adverbials, and create the context for the whole sentence.

See these example sentences using disjuncts:
- “Apparently there is nothing that cannot happen today.” -Mark Twain
- “Basically my wife was immature. I’d be at home in the bath and she’d come in and sink my boats.” – Woody Allen
- “They’re plainly both skilled at concealing their real selves from the world, and they’ve presumably managed to keep their respective secrets from each other,” (Frayn, 2009).
- “It rarely adds anything to say, ‘In my opinion’—not even modesty. Naturally, a sentence is only your opinion; and you are not the Pope,” (Paul Goodman 1966).
(Quotes are from Definition and Examples of Sentence Adverbs in English on ThoughtCo)
Other Examples of sentence adverbs include words like:
- actually
- apparently
- basically
- briefly
- clearly
- ideally
- indeed
- similarly,
- hopefully,
- luckily
- incidentally,
- interestingly,
- predictably,
- presumably,
- strangely,
- surprisingly
- obviously
Adverb modifying adverbs
Think, adverb-ception (the second attempt at a bad grammar joke from a previous article which used, quote-ception.) In some sentences, an adverb modifies another adverb.
Adverbial phrases & verb phrases
Adverbs can also take the form of a group of words or clause in a sentence. As a group or phrase, they help express emphasis or specificity in or around the sentence verb.
An adverbial phrase is a group of words that function as an adverb and modifies other parts of speech.
Examples of adverbial clauses and phrases include:
- The carpenter hit the nail with a hammer.
- Jodie buys two CDs every month.
- The woman who lives next door is a doctor.
See in the sentences above how adverb clauses describe or modify adjectives, events and actions by saying more about them.
Frequency/infrequency adverbs
Adverbs of frequency and infrequency tell us how often the action or event occurs. Such adverbs respond to questions like, ‘how often.‘
The six main adverbs of frequency are: always, usually (or normally), often, sometimes, rarely, and never.
By seeing these words in action in various sentences, it’s clearer how the words function to display a range or degree of frequency/infrequency.
See the following sentences that use temporal adverbs as an example:
- Sara always goes out on Saturday evenings.
- Jane’s boyfriend usually picks her up, and they drive into the city center.
- Ben and Emma often go for lunch together.
- In the winter Sara sometimes goes Skiing in France.
- James and Stephen rarely go to the cinema in the summer because they prefer to stay outside.
- As Marta is so busy, she never gets home from work before 7
Example sentences are from ThoughtCo‘s, “What is an adverb of time?”
Adverbs that illustrate definite frequency are words like weekly, daily, monthly, and bi-weekly. They refer to a definite or set period of time, and are unambiguous. For example:
We swim weekly at the community center; we attend the golf club events monthly.
Indefinite frequency adverbs, on the other hand, do not point to a specific or set timeframe. Examples of these words includes usually, sometimes, rarely, occasionally, frequently, infrequently, and so on.
Adverbs of time can refer to either a definite time (i.e., ‘I’ll do it next Monday,’) or an indefinite time, (i.e., ‘We usually go to Rome around spring.’)
Common adverbs of frequency includes:
- always,
- constantly,
- infrequently,
- generally,
- hardly ever,
- never,
- normally,
- occasionally,
- often,
- rarely,
- regularly,
- sometimes and
- usually.
Place adverb or adverb of place
Adverbs of place, sometimes referred to as spatial adverbs describe where actions occur. They help answer the adverb question, ‘where?’
Place adverbs give information about the position of an action, (north, south, east, southeast,) direction; and distance. These adverbs are extremely common in English.
Here are a few examples of adverbs that modify verbs, (i.e., spatial adverbs) includes: above, anywhere, behind, below, downward, everywhere, forward, here, in, inside, left, near, outside, over there, sideways, underneath, and upward.
In sentences, place adverbs appear directly after the verb or action they modify (or contextualize.)
See these sentences as examples where place adverbs modify verbs:
- Matt searched around his house, but he still couldn’t find his glasses.
- Come over here and look at what I found!
- I searched everywhere I could think of.
- Television programs produced in New York and Hollywood are seen worldwide.
- I heard a nightingale singing somewhere not far away.
- “Just picture a penthouse way up in the sky,
With hinges on chimneys, for clouds to go by.”(Val Burton and Will Jason, “When We’re Alone”) - “Emerging from the wood, she skirted past the far side of the bowling green and walked down the steps of the sunken rose garden and out the other side.”
(Alison Prince, “The Water Mill.” The Young Oxford Book of Nightmares. Oxford University Press, 2000)
Example sentences are from ThoughtCo‘s article.
The adverbs tell us where the action happens. Many adverbial phrases are made up of a spatial adverb and a preposition; for example, ‘What are you doing up there?’
Auxiliary verbs and helping verbs
Wikipedia defines the auxiliary verb as “A verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc.)”
Origin of the word adverb
The word adverb derives from the Latin phrase, adverbial. The term is called adverbs as a truncated or shortened version or the original Latin phrase.
Check out another article
Is there a comma before while? When does the word “while” have a comma before it?
What’s an Oxford comma (serial comma)? When is it necessary to use, and when not to use it?
Curious to know whether it’s fullproof, full proof or fullproof? What about beckon call or beck and call? Learn the difference and master the art of English prose.
Positive adverbs list
- boldly
- bravely
- brightly
- cheerfully
- deftly
- devotedly
- eagerly
- elegantly
- faithfully
- fortunately
- gleefully
- gracefully
- happily
- honestly
- innocently
- kindly
- merrily
- obediently
- perfectly
- politely
- powerfully
- safely
- victoriously
- warmly
- vivaciously
Negative adverbs list
- achingly
- angrily
- annoyingly
- anxiously
- badly
- boastfully
- dejectedly
- enviously
- foolishly
- hopelessly
- irritably
- jealously
- joylessly
- lazily
- miserably
- morosely
- obnoxiously
- painfully
- poorly
- rudely
- sadly
- selfishly
- terribly
- unhappily
- wearily
Grammar rules in review
Adverbs perform various responsibilities in language and grammar. Adverbs modify adjectives, verbs, phrases, and other adverbs, adverbs tell us key information and details about actions and other parts of speech.
Adverbs can be single words or a group of words or phrase.
What about exceptions to the rules?
As always with English grammar, there are many exceptions to to the rules of adverbs.
Glossary and Sources
- Adverb: A word that describes or gives more information about a verb, adjective, adverb, or phrase: In the phrase “the house was spotlessly clean”, the word “spotlessly” is an adverb. (Cambridge Dictionary.)
- Adverbial phrases: “its syntactic function is to modify other expressions, including verbs, adjectives, adverbs, adverbials, and sentences. Adverbial phrases can be divided into two types: complement adverbs and modifier adverbs (Wikipedia). Also see Wikipedia on Adverbials: is a word (an adverb) or a group of words (an adverbial clause or adverbial phrase) that modifies or more closely defines the sentence or the verb
- Sentence adverbial: “an adverb that limits or describes the meaning of an entire statement rather than just a single word or phrase “Similarly” and “hopefully” often function as sentence adverbs.” From https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/sentence%20adverb
- Disjunct: “a disjunct is a type of adverbial adjunct that expresses information that is not considered essential to the sentence it appears in, but which is considered to be the speaker’s or writer’s attitude towards, or descriptive statement of, the propositional content of the sentence, “expressing, for example, the speaker’s degree of truthfulness or his manner of speaking.” (Wikipedia, on disjunct, from Brinton, Laurel J. and Brinton, Donna,The Linguistic Structure of Modern English John Benjamins Publishing Company, 29 Jul 2010, p. 219.[1]
- Locative adverb: “A locative adverb is a type of adverb that refers to a location or to a combination of a location and a relation to that location.” (On Wikipedia)
- Adverbs of time: “adverb (such as soon or tomorrow) that describes when the action of a verb is carried out. It can also be called a temporal adverb.” (from ThoughtCo’s “What is an adverb of time?”)
- Adverbs of frequency: from “How to teach adverbs of frequency in English” as seen on, https://www.wallstreetenglish.com/blog/how-to-teach-adverbs-of-frequency-in-english
- Auxiliary verbs: “adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause.” (as defined on Wikipedia, cited The Oxford English Dictionary, Second Edition, defines an auxiliary verb as “a verb used to form the tenses, [grammatical mood/moods], [grammatical voice/voices], etc. of other verbs.” OED Second Edition, 1989. Entry for auxiliary).
- Flat adverbs: “a flat adverb, bare adverb, or simple adverb[1] is an adverb that has the same form as the corresponding adjective,[2] so it usually does not end in -ly, e.g., “drive slow,” “drive fast,” “dress smart,” etc. The term includes words that naturally end in -ly in both forms, e.g. “drive friendly.” (from Wikipedia, O’Conner, P.T.; Kellerman, S. (2009). Origins of the Specious: Myths and Misconceptions of the English Language. Random House Publishing Group. p. 30. ISBN 9781588368560; Garner’s Modern American Usage, p. 897; “Drive Safe: In Praise of Flat Adverbs” with Emily Brewster, part of the “Ask the Editor” series at Merriam-Webster.com)
- Definition of adverb: dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/adverb
- Example quotes: thoughtco.com/sentence-adverb-1692084
- Spatial adverbs examples: thoughtco.com/adverb-of-place-1691512
- Auxiliary verb: wikipedia.org/wiki/Auxiliary_verb
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



