Recurring vs. reoccurring, what’s the difference? If something is recurring, isn’t it the same as if it’s reoccurring? A recurring event or a reoccurring event? These two words sound similar, though have two separate meanings in American English. Both are similar in pronunciation, spelling, and meaning—making it confusing for writers.
Learn what recurring and reoccurring mean in this short guide…
A short history of the word reoccur (or recurring)
The first mention of the word “reoccur” came in Francois Fenelon’s The Adventures of Telemachus. Translator John Ozell notes, “the same objects frequently re-occur in this poem.” The date of this publication was 1734, making the word appear relatively early in the English language.
Recurring definition and meaning
Recurring is the adjective of the noun recurrence. Or the root word “recur.” Merriam-Webster defines recurring as something “recurring repeatedly.” Or “happening or appearing multiple times.”
Something recurrent tends to suggest that it is something that “comes back having never existed before.” Rather than recurring, which implies a repeated occurrence.
Simply put, something recurring implies that it will continue to occur on an ongoing basis. For example, “The paycheck comes on the 15th of every month. It is a recurring event.”
Synonyms of recurring
- Continual
- Intermittent
- On-and-off
- Periodic
- Recurrent
Antonyms
- Constant
- Continuous
- Unceasing
Example sentences
“I keep having this recurring dream that I will wake up and have a bed full of snakes. I understand that it’s not real. Although it is scary.”
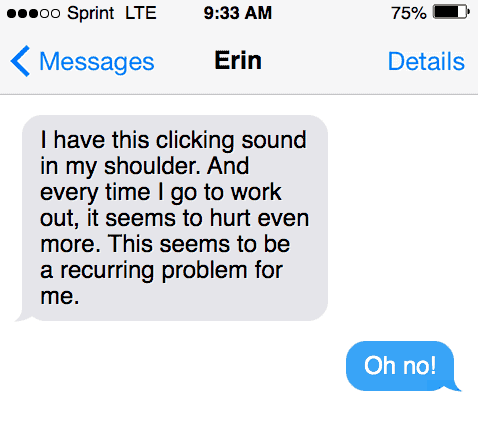
“I have this clicking sound in my shoulder. And every time I go to work out, it seems to hurt even more. This seems to be a recurring problem for me.”
“My doctor says I must come back every 6 months to get this looked at. It could be a recurring issue that comes back periodically.”
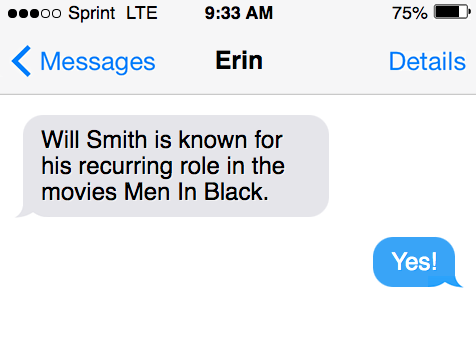
“Will Smith is known for his recurring role in the movies Men In Black.”
In these examples, we are using the word recurring to say that something will “recur.” Recur means to happen repeatedly or after an interval of time.

Reoccurring definition and meaning
Something that is reoccurring is “to happen another time” according to Merriam-Webster. When something is reoccurring, it means that it has already happened once and happens again. Although, it doesn’t necessarily mean that it happens frequently.
When something is reoccurring, there isn’t an expectation that it will continue to happen. For example, someone who would like to make a meal a second time would be a reoccurring meal. For example, “I think I’ll make the deep dish pizza once more.”
If something happens frequently, repetitively, or at regular intervals—it is better to use recurring rather than reoccurring.
What about reoccurring events and recurring events?
Reoccurring events would be things like presidential elections. While recurring events would be things like the alarm going off every morning at 8 am. Or another example would be a subscription. Someone would get charged at regular intervals, making it a recurring event.
The key difference when referring to events is that something that reoccurs happens again, but not necessarily repeatedly.
Example sentences
“I had a weird dream the other night. And it’s odd because I had this dream once before. I wonder if it is reoccurring. We will find out in the future.”
“I don’t know if I’m going to get diagnosed with a reoccurring illness. I went to the doctor, and there’s no information for me yet.”
In these examples, we are using reoccurring because it is a case where something has happened once and may happen repeatedly. Although, in both examples, it is uncertain whether it will or not.
Reoccur in sentences
When something is past tense, it is sometimes referred to as something that may “reoccur.” Here are example sentences showing the past tense form of the root word and verb (re + occur).
The word reoccur comes from the prefix “re” and the verb occur to create “reoccur.”
“After the financial crisis in 2008, banking systems and the federal reserve created safe measures in place to ensure that something would not reoccur again.”
“The crash happened multiple times last year, making it one of the most severe cases in the United States. Preventative measures are being put in place to ensure this doesn’t reoccur again.”

Base forms of recurring and reoccurring
To remember which word to use, remember these base forms:
Recurring: For something to recur.
Reoccurring: For something to reoccur.
What are base forms?
Recurring vs reoccurring: key differences
Here are the key differences between recur and reoccur:
When something could recur: Something that has happened once, although may not happen again on a regular basis. For example, “While the symptoms for a chronic illness may recur, we have put preventative measures in place.”
When something could reoccur: Meaning that something has happened regularly and may continue to happen. Reoccur means it is expected to continue happening. For example, “Will Smith is appearing on the new TV Show, Quiz. This will reoccur every week for 52 weeks.”
By understanding these two terms, we can use recurring and reoccurring correctly. When we want to refer to something happening regularly, we should use the correct spelling of that thing being “reoccurring.”
When we think of something that has happened, although it may not happen again, we would want to imply that it’s unknown, or that it may not “reoccur.”
Difference examples
“I wanted to make a great steak the other night. I want to make this a reoccurring meal for the rest of the family.”
“I want to make a great steak every Tuesday. It could be a great recurring meal for us to make a better life.”
In both forms, the writing refers to something that happens again.
How to remember to write recurring vs. reoccurring
To have something repeat is the closest synonym for something reoccurring.
When something repetitive is recurring.
If something recurs, it happens regularly, at an expected time and case.
Tricks to remember
When something repeats after it happened once, it may become a surprise if it is reoccurring. The “o” in the word is the surprise part.
If something continues to happen, it wouldn’t be surprising the second time, meaning there is no reason for the “o.” Think of the letter “o” as “Oh!” A type of surprise.
Adjectives
- Recurring
- Recurrent
- Reoccurring
Verbs
- Recur
- Recurs
- Reoccur
- Reoccurs
Past tense verbs
- Recurred
- Reoccurred
Nouns
- Recurrence
- Reoccurrence
What’s the best form to use when in doubt?
When in doubt, the best word to use is recurring. Most commonly, you are referring to something recurring. For example, a recurring theme. Or a recurring character. And lastly, a recurring payment.
Sources
- Les Aventures de Télémaque – Wikipedia
- Recur Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
- Reoccur Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
- 12 Synonyms of REOCCUR | Merriam-Webster Thesaurus
- RECUR | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary
- Best 12 Definitions of Recur – YourDictionary
- Base Verb Definition and Examples – ThoughtCo
- BASE FORM | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate