What is a misplaced modifier? It’s important to be be aware of a misplaced modifier. Why is that? Well, because by comprehending what a misplaced modifier is, it will help you write clear sentences. And will allow you to explain your thoughts, ideas, concepts, and intentions with depth and understanding.
A dangling and misplaced modifier will absolutely confuse your readers. It can also make the sentence you wrote appear quite odd. This guide will help you garner better clarity on misplaced modifiers and how to fix them.
What Is a Misplaced Modifier?
The meaning and its difference are:
Definition
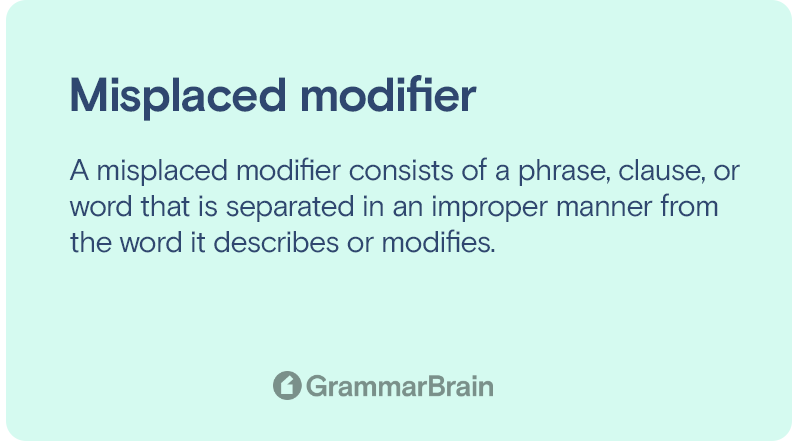
A misplaced modifier consists of a phrase, clause, or word that is separated in an improper manner from the word it describes or modifies.
Sentences containing this error usually sound confusing and awkward as a result of the separation. Plus, they can sound wholly illogical and ridiculous, too.
Let’s describe this with an example:
- Tenzing Norgay made history as the first man to reach the summit of Mount Everest in 1953.
Here, the sentence sounds like Tenzing Norgay were the first man to reach the summit of Mount Everest in that specific year. It appears so because of the modifier placement in 1953.
Instead, the placement of the modifier should be directly right next to the clause it relates to. So, it should go like ‘Tenzing Norgay Made History.’
The correct way to use the modifier is as follows:
- In 1953 Tenzing Norgay made history as the first man to reach the summit of Mount Everest.
- Tenzing Norgay made history in 1953 as the first man to reach the summit of Mount Everest.
Difference Between Dangling Modifier
It is pretty common to make mistakes between dangling and misplaced modifiers. Here, both of these terms consist of modifiers, which are connected to the wrong thing within a sentence.
The intended subject of a dangling modifier is missing altogether from the sentence. On the other hand, a misplaced modifier happens to be very distant from the thing or element it intended to modify.
Let’s take the explanation further with some examples:
Misplaced Modifier Example
Examples of a misplaced modifier:
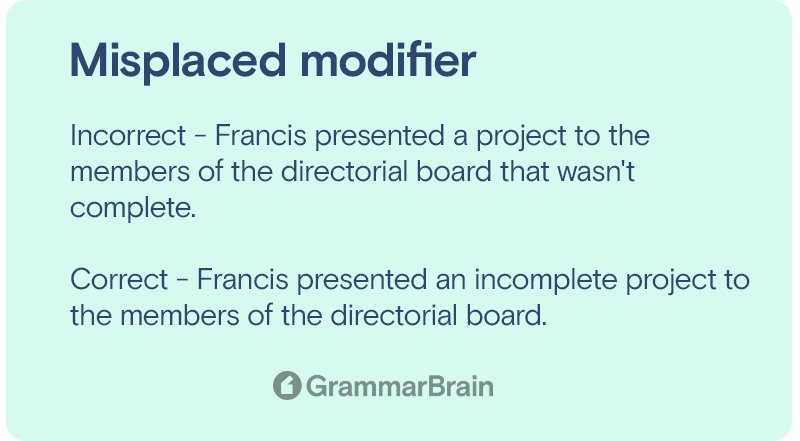
- Incorrect – Francis presented a project to the members of the directorial board that wasn’t complete.
- Correct – Francis presented an incomplete project to the members of the directorial board.
- Correct – Francis presented a project that was incomplete to the members of the directorial board.
Dangling Modifier Example
Examples of a dangling modifier:
- Incorrect – Fumbling in his bag, the wallet could not be found.
- Correct – Fumbling in his bag, he could not find the wallet.
- Correct – As he fumbled in his bag, the wallet could not be found.
| Dangling Modifier | Misplaced Modifier |
| Found at the front of sentences. | Found within or at the ends of sentences. |
How To Avoid Confusion from a Misplaced Modifier
Modifiers include words-adjectives, prepositional phrases, adverbs, and clauses that enrich, explain, and expand sentences. The misplaced modifiers need to be shifted elsewhere within the sentence to avoid potential confusion.
The outcome of misplaced modifiers tends to be comedic and confusing. Here, most comedians deliberately take advantage of them.
We will list the 4 Golden rules for the correct placement of these modifiers. These will help in getting rid of most of the confusion you could face on a misplaced modifier:
Simple Adjectives Precede
Let us use an example here:
Jordan set a bowl of aromatic soup too steep on the kitchen countertop while she pulled the fluffy hat over his cold feet.
- Aromatic is modifying soup.
- Fluffy is modifying hat, and
- Cold is modifying the feet.
The adjective modifier ends up preceding the noun that it modifies. Because it isn’t ‘Soup Aromatic’ but ‘Aromatic Soup.’ The same applies to the other modifiers in the sentence.
Adjective Phrases and Clauses Follow
It is common for us to associate the phrase modifiers with the closest preceding nouns.
- Incorrect – The swimming trainer dove into the pool with the deep tan.
- Correct – The swimming trainer with the deep tan dove into the pool.
The example mentioned above possesses a comic effect. It’s because we are reading the modifier, i.e., ‘With the Deep Tan,’ as it belongs to the closest noun.
Adjective phrases like this don’t just follow the nouns they describe. They should follow in a close manner (or proximity) to provide proper clarity.
The adjective clauses should also get treated similarly. These word groups possess both a verb and a subject.
However, they aren’t complete because they feature a dependent-creating or “making” a type of word. They are known for explaining or expanding on information within the sentence.
Plus, they should instantly follow their required headwords like adjective phrases.
Adverbs Move Around
Adverbs are known for modifying other adverbs, verbs, and adjectives. Adverbs can move around in sentences without issues.
Take an example here:
- Quickly he calculated the sum and summarized the answer.
- He quickly calculated the sum and summarized the answer.
- He calculated the sum and quickly summarized the answer.
- He calculated the sum and summarized the answer quickly.
From the examples, the adverb ‘Quickly’ modifies the verbs ‘Summarized’ and ‘Calculated.’ It does so without causing any confusion, regardless of its placement.
But misplaced adverbs, on the other hand, tend to cause ambiguity. When it happens, proceed in simply moving the adverb to place it right next to a headword that its’ intending to modify.
Adverbs tend to “squint” because of their ability to float around freely in a sentence. Squinting adverbs have a reputation for modifying 2 things simultaneously.
A sentence containing the squinting adverb appears to mean or portray one thing at first and then another. It’s almost like an optical illusion.
Also, adverb clauses express relationships like time, condition, cause, and purpose. It uses words such as when, if, because, and so on.
The adverb clauses have no trouble moving around within a sentence.
Limiters Precede
Here, limiters consist of words such as ‘hardly, ‘ only, ‘almost,’ ‘nearly,’ and ‘just.’ The placement of these words should be in front of the headwords.
Look at the difference in meanings from the following examples:
- Sergio does English homework almost every single day.
- Robert almost does English homework every day.
Were you able to spot the difference between the two sentences? The first does his English homework, while the second doesn’t.
Almost doing the English homework sounds nonsense. In the first sentence, ‘Almost’ is modifying ‘Every’, and the second sentence consists of ‘Almost’ modifying ‘Do.’
The second speaker doesn’t do his English homework. He is ready and thinks about doing it but doesn’t do it.
It’s incorrect unless the intended meaning behind it is deliberate.
| Dangling Modifier Example | Misplaced Modifier Example |
| Incorrect: In the fishbowl, Sally fed the fish. Correct: Sally fed the fish in the fishbowl. | Incorrect: Tom drove to school in his car. Correct: In his car, Tom drove to school. |
Examples of a Misplaced Modifier
Here are some examples of a misplaced modifier:
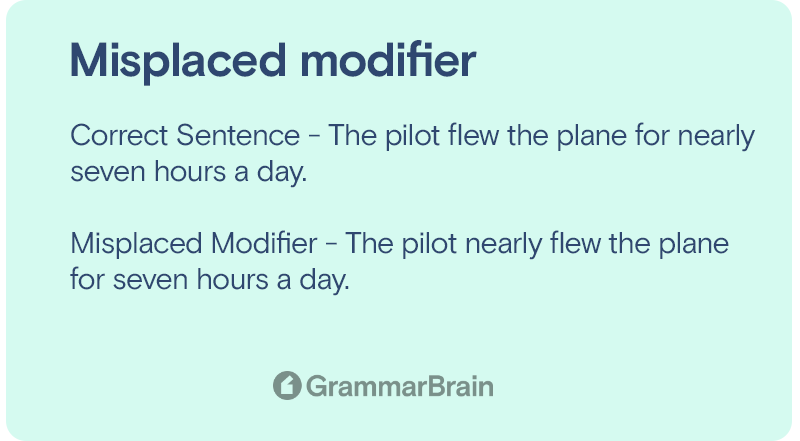
Correct Sentence – The pilot flew the plane for nearly seven hours a day.
Misplaced Modifier – The pilot nearly flew the plane for seven hours a day.
Correct Sentence – My neighbor gave me only $10 to clean all of his backyard.
Misplaced Modifier – Only my neighbor gave me $10 to clean all of his backyard.
Correct Sentence – Billy almost lost every game he played.
Misplaced Modifier – Billy lost almost every game he played
Correct Sentence – Folks who rarely talk are introverted in nature,
Misplaced Modifier – Folks who talk rarely are introverted in nature.
Correct Sentence – Eagerly awaiting his graduation day, Nick picked up and started admiring his outfit multiple times throughout the day.
Misplaced Modifier – Eagerly awaiting his graduation day, Nick’s suit was picked up and started admiring by him multiple times throughout the day.
Correct Sentence – Exhausted by all the constant traveling, Susan was overjoyed when her boss finally told she didn’t have to travel anymore.
Misplaced Modifier – Exhausted by all the constant traveling, joy overcame Susan when her boss finally told she didn’t have to travel anymore.
Correct Sentence – Jude bought a cat called Meredith for his sister.
Misplaced Modifier – Jude bought a cat for his sister called Meredith.
Correct Sentence – He served the orphans pies on paper plates.
Misplaced Modifier – He served pies to the orphans on paper plates.
Correct Sentence – On the way home, he saw a Jason and his grandmother.
Misplaced Modifier – He saw Jason and his grandmother on the way home.
Correct Sentence – The Orange County Police reported that five banks were robbed last month.
Misplaced Modifier – Five banks were reported robbed by the Orange County Police last month.
How To Fix a Misplaced Modifier
It’s not that difficult to fix a misplaced modifier. You can correct it by moving the modifier to a more sensible place within the sentence.
Generally, it should be placed next to the word it is modifying. Let’s demonstrate this fix with an example of our own:
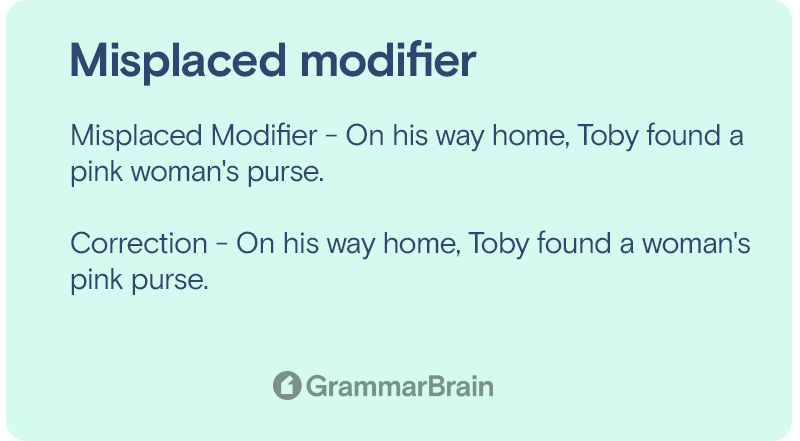
- Misplaced Modifier – On his way home, Toby found a pink woman’s purse.
- Correction – On his way home, Toby found a woman’s pink purse.
If you look at the first sentence, it depicts that the purse belongs to a pink woman. But when you change and position the modifier, the sentence makes sense.
FAQs
What Is an Example of a Misplaced Modifier?
Misplaced Modifier Sentence – Lilith was praised for her achievements by her professor.
Correction – The professor praised Lilith for her achievements.
What Is a Misplaced Modifier?
A misplaced modifier consists of a clause, word, or phrase placed far from the words or words it modifies.
How Do You Find Misplaced Modifiers?
You can identify one when the adjectives are separated incorrectly from the nouns they modify. The sentence will have a distorted meaning, causing it to sound funny or vague.
What Is a Modifier in a Sentence?
Modifiers refer to words, clauses, or phrases responsible for affecting and improving the meaning of sentences.
Are misplaced and dangling modifiers the same?
They are very similar when used in common sentence structure. A modifier is a word or phase that modifier the wrong thing because of the intended subject missing from the sentence. Using them correctly ensures a clear sentence structure. A dangling modifier will make your sentence unclear.
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



