What’s the difference between curricula vs curriculum? Confusion emerges over the plural forms of the word curriculum since its plural ‘curricula‘ (the most popular plural form) derives from a Latin word, and aboriginal English speakers are uncertain whether to use curricula or curriculums as the plural form. This is because curriculums adhere to the formal ruling for creating plurals, which has come into use.
Several Latin-rooted words (for example, referendum, stadium, and nucleus) have either embraced a typical plural ending the Latin one alongside or have entirely declined the Latin one (for example, referendums but referenda). While a few have entirely maintained their Latin plural (for example, stimuli but stimuluses).
And with the word curriculum, both curricula and curriculums are acceptable. Now let’s figure out the main difference and usage of curricula vs. curriculum.
Grammatical Explanation of Curricula and Curriculum
Curriculum and curricula describe a single course of study and a set of courses for students simultaneously. Nevertheless, there is a fine line between these two words.
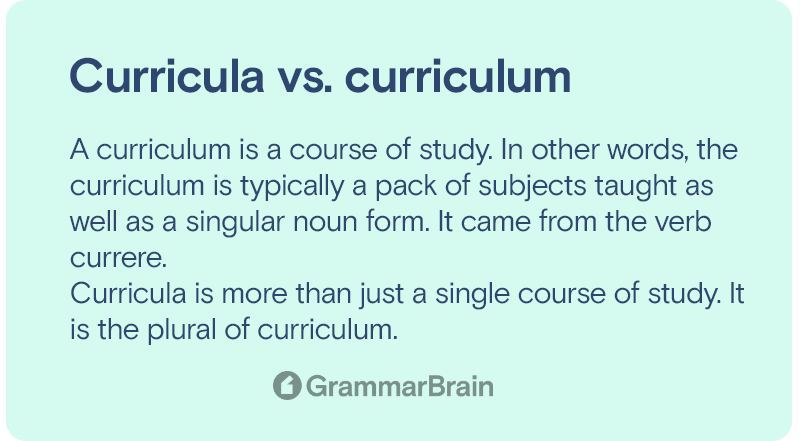
- A curriculum is a course of study. In other words, the curriculum is typically a pack of subjects taught as well as a singular noun form. It came from the verb currere.
- Curricula is more than just a single course of study. It is the plural of curriculum.
Similar to other Latin noun words that generally end in the letters -um, the word curriculum takes the form curricula in the plural noun.

Difference Between Curriculum vs Curricula
Here we are going to compare curricula vs curriculum in this post below. We will also provide a few example sentences that will give you a vivid idea of how the words should appear in lesson plans.
Let’s get started..
Meaning of Curriculum: A Course of Study
The curriculum describes assessments, lessons, materials, assignments, and readings in a single study course.
A Few Examples In Sentences:
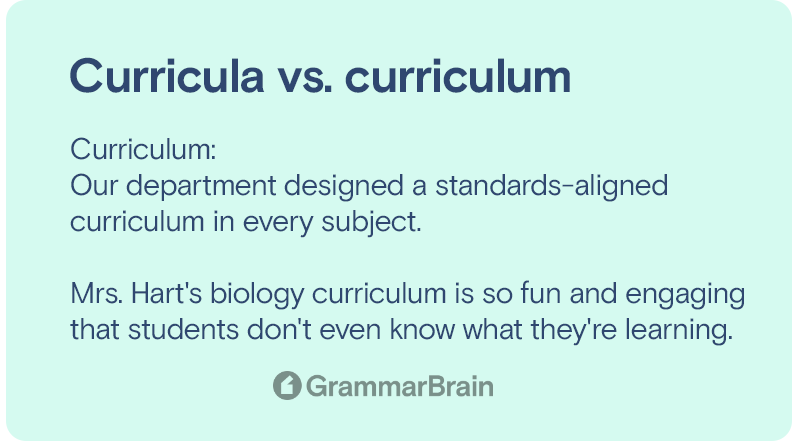
- Our department designed a standards-aligned curriculum in every subject.
- Mrs. Hart’s biology curriculum is so fun and engaging that students don’t know what they’re learning.
- Have you finished writing the math curriculum for 11th grade?
- The school board approved a new curriculum that integrates 21st-century skills into the classroom.
- The typical language arts curriculum in kindergarten includes phonics, sight words, and handwriting practice.
Meaning of Curricula: Numerous Study Courses
The plural form of ‘curriculum’ is either ‘curriculums’ or ‘curricula.’ ‘Curricula’ is commonly used to resemble different study methods or highlight that an institute has more than just one curriculum.
A Few Examples In Sentences:
- Before declaring your university major, a wide range of curricula are available for you
- When you prepare 5 different classes, you will also have to master 5 different curricula.
- Let’s plan the 3rd-grade & 4th-grade curricula together. This will help us avoid teaching the same topics.
- Can you create curricula for every primal reading level?
In summary
Even if you aren’t a Latin teacher, having a common idea of how a Latin word works in English can help you. After all, designing a single set of curricula is much more distinct than preparing a series of curricula!
If you need guidance on preparing a top-notch curriculum, you need to check out some lesson program templates to ensure your students are getting their objectives.
FAQs
What is the difference between curricula vs curriculum?
Curriculum is the singular form, while ‘curricula’ is the plural form of the word curriculum. For example:
Curriculum- The school board has approved a new curriculum with 21st-century mastery in the classroom.
Curricula- You always need to keep your curricula updated.
What Is the plural of the curriculum?
There are two words for the plural form of curriculum. The most popular plural ‘curricula’ is the one people commonly use worldwide. While the other plural form, ‘curriculums,’ is a lesser-known one. However, both curricula and curriculums are correct.
What is the meaning of curricula?
The words curricula & curriculum come from a Latin word that describes another type of course. Curricula are the topics in a particular course of study at universities or other higher educational institutions.
Can you say curriculums?
The plural form of the word curriculum is also curriculums. Both curricula and curriculums are correct plural forms of the word curriculum. However, in the formal English language and academic settings, it is better to use curricula while describing numerous sets of your curriculum.
You should use curricula for more than one course and curriculum for a single course of study.
Is curricular plural?
Curricula is the plural form of curriculum. For example, you need to keep your curricula updated with your value-based education.
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



