‘Bear with me’ is a common phrase often mistaken for ‘bare with me.’ It’s critical not to mistake the two since ‘bear with me’ is right, and ‘bare with me’ is wrong. ‘Bare’ and ‘bear’ are two different words with completely distinct meanings and uses in the English language. This is true whether communicating in writing or verbally, so let’s make sure to use the correct expression.
It takes time to learn how to write in English and to ensure writing is error-free. Do not get discouraged; rather, embrace these learning opportunities for the challenges they provide. Bear the language learning process for what it is. After all, practice makes us better and stretches our skill sets beyond what we thought possible. Keep reading to understand the key differences between both words and phrases.
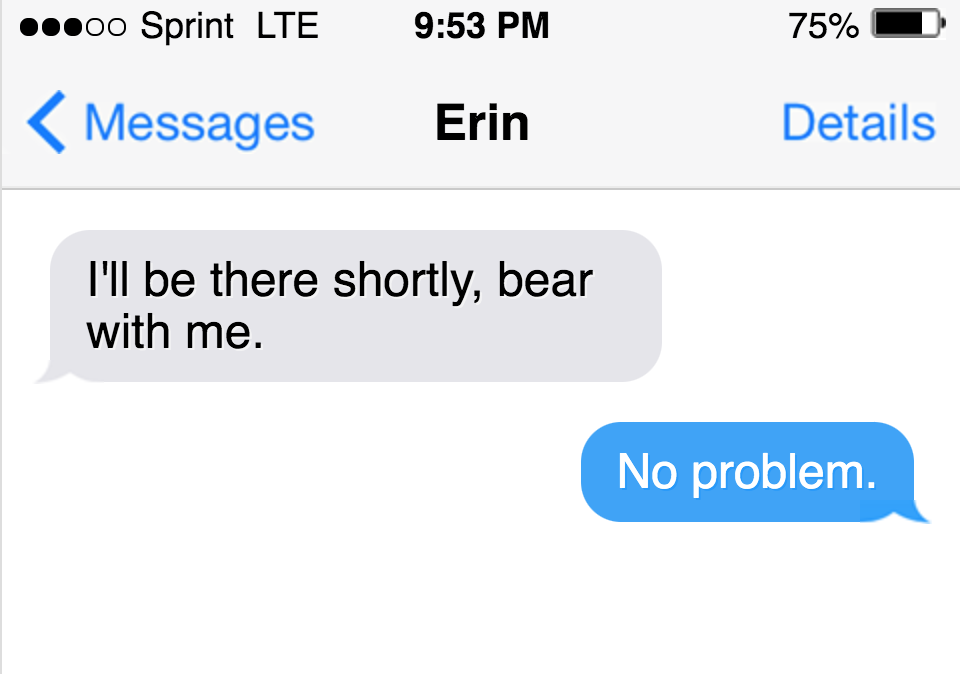
Is it ‘bear with me’ or ‘bare with me’?
‘Bare with me’ may sound correct, but it is, in fact, wrong. The correct spelling is ‘bear with me,’ not ‘bare with me.’ Consider these examples that illustrate the right and wrong uses of these phrases.


What does ‘bare’ and ‘bear’ mean?
Learn the difference between ‘bare’ and ‘bear.’
The meaning of ‘bare’
The phrase ‘bare‘ means to uncover, reveal or expose something. These sentences are grammatical ways to write ‘bare’:
“He was bare naked from the waist up”
“We only brought the bare bones for our week-long canoe trip; this way, the packs wouldn’t be too heavy”
“The girl woke up bare-faced, rosy-cheeked and full of purpose.”
These are all expressions of the phrase ‘bare’ meaning to reveal, uncover or expose.

The meaning of ‘bear’
The verb ‘bear’ is a homophone (homophones are words that sound the same and are spelled the same, but have different meanings.) In this sense, the verb ‘bear’ refers to being able to endure or tolerate a tough situation. This should not be confused with the noun ‘bear’, like a Polar bear, (the white furry, carnivorous mammal that lives in the Arctic).
What are homophones?
Homophones may sound complicated, but it’s usually easy to distinguish between the correct use of homophones based on the context in which they’re used. It’s easy to get confused when learning, but it’s merely a matter of practice and consistent exposure before it is easy.
Another instructive example of a homophone is the word ‘sound‘. Based on how it’s used, the meaning that’s intended is clear and intuitive, though entirely distinct.
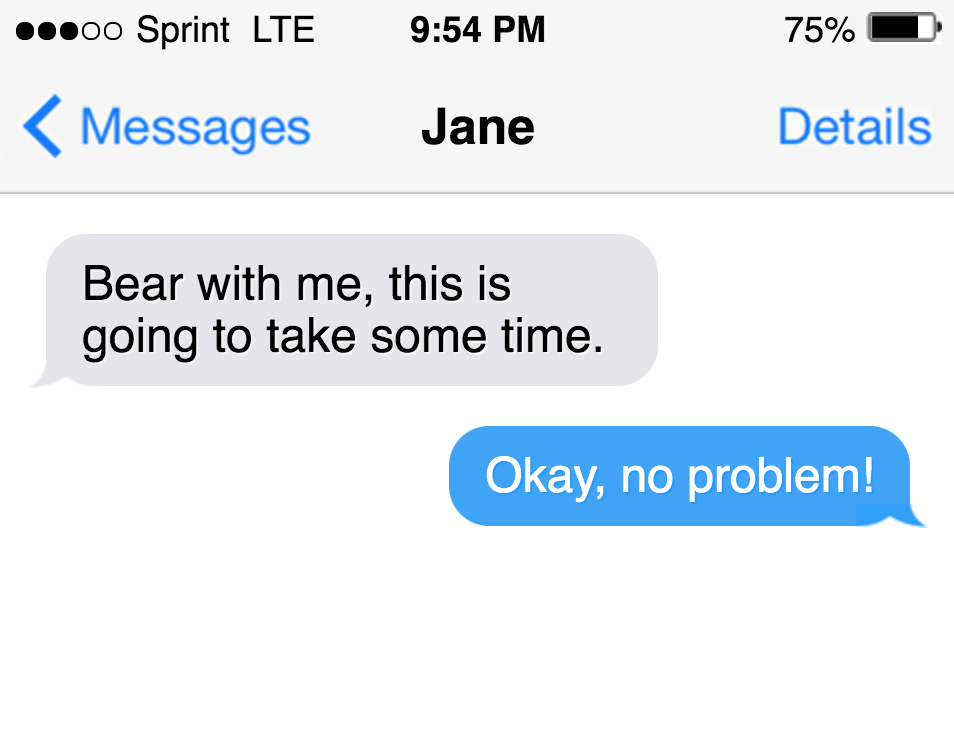
Consider these examples that use various interpretations of ‘sound‘:
“It was a sound decision to attend the practice rehearsal.”
“The sound of the waves crashing soothes me.”
It’s clear from the above that the same word can mean different things entirely based on the context in which they’re used, despite being phonetically indistinguishable from each other.
In the first sentence, the intended meaning of the word ‘sound’ is to be rational or reasonable in one’s decision-making.
Whereas in the second sentence, the word ‘sound’ refers to the more common use of the word that describes a loud noise or something audible that we can hear.
Bonus fact! Transitive verbs are parts of a sentence that require direct objects or receivers of the action of the verb.
Example: Sam gave the pen to his friend to borrow for class.
The word ‘gave‘ counts as the transitive verb in the sentence, since this word is associated with a direct object.
The meaning of ‘bear with me’
In the phrase ‘bear with me,’ ‘bear‘ has various definitions and can be used as a noun and a verb. As a verb, ‘bear’ means to endure or deal with a difficult situation. It’s clear that the use of the verb ‘bear’ here does not refer to a wild animal, i.e., a grizzly bear.
To ‘bear with me’ is the right spelling and expression to ask a person to have patience, or to be patient while getting through a burden or difficulty.
The correct uses of ‘bear with me’ examples
Look at the following correct uses of the phrase ‘bear with me.’
- “I apologize for the delayed response. I hope you will bear with me. It’s been a tough time.”
- “I couldn’t bear to see the person I love in such a sad and miserable state.”
- “I realize you’ve waited a long time to get your test results. If you can continue to bear with me, it shouldn’t take much longer until we receive the test results.”
- “I couldn’t bear the cold and harsh Canadian winters any longer, so we decided to move to Arizona.”
How to remember to use ‘bear with me’?
To readily recall the proper use of ‘bear with me,’ keep in mind this mnemonic:
“The bears bear the winter.”
The phrase ‘to bear with’ is spelled and sounds the same as the word ‘bear’ the animal. The wild grizzly bear, Black bear and Polar bear must bear through the winter. “Bears that don’t bear you may eat you” (there’s another way of remembering the spelling.)
That’s it—just think of Polar bears bearing the winter, and the spelling of the phrase ‘bear with me’ will be intuitive and second nature in no time.
Other ways of saying ‘bear with me’
The expression ‘bear with me’ can be described through other words too. Phrases and words that express the same idea are called synonyms. Here’s a look at a few synonyms of the expression ‘bear with me’:
“I appreciate your patience”
“Hold tight”
“Endure this with me”
“Brace yourself for this”
Put simply, ‘bear with me’ means to endure, to tolerate and be patient, despite not wanting to. Some of the synonyms like, “hold tight”, have a more conversational tone. Nevertheless, they communicate the same underlying idea of having to endure or tolerate an uncomfortable experience.
Sources
- Meaning of synonym in English – Cambridge Dictionary
- Polar Bear | Species | WWF – World Wildlife Fund
- American black bear – Wikipedia
- Transitive and Intransitive Verbs – Grammar – Academic Guides
- Top 20 Most Commonly Confused Homophones – Scholastic
- Phrase Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
- Mnemonic – Wikipedia
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



