What is a definite article? When spoken or written English is used to communicate effectively, the use of articles often occurs. These are important components of writing, as they specify the noun they precede as “particular” or “general.” The noun, depending on its conveyed meaning, uses the article placed before it, to relate its meaning to the reader or listener. There exist two articles in English. The definite article and the indefinite article.
What is the definite article?
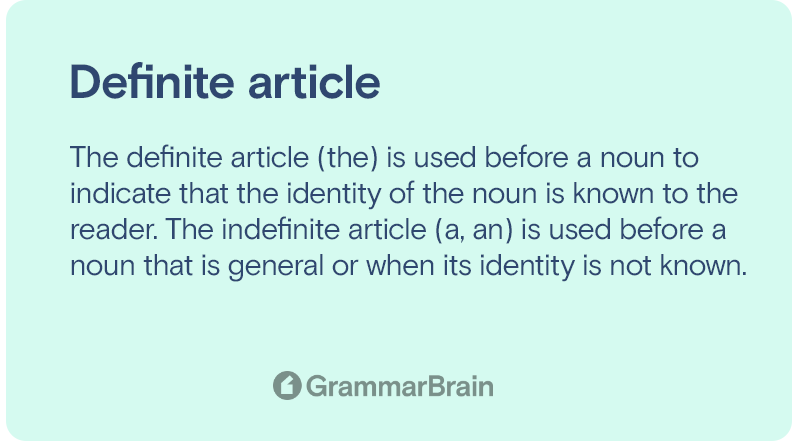
In English, the definite article is the word “the.” Called the definite article, it specifies a noun in particular. When something “definite” about the noun has to be stated, the definite article “the” is employed. In English, this comes before the noun that it relates to.
Consequently, some instances of use include phrases like this:
- The actor
- The school
- The film
- The book

Definition
The definite article is the word “the” in English. In its simplest definition, it is a word used before any noun and indicates the noun’s identity.
Through this expression of the noun, the identity of the noun becomes known to the reader or the listener. In contrast, when a noun does not have to be particularly or specifically identified, another article, the indefinite article is used.
The definite article is “definite” because it implies something “definitive” about the noun. In terms of its basic use, the following examples indicate how the definite article exists in text:
- The book is on the table.
- The lily grows tall in spring.
- Today, the snow fell heavily in the hills.
- The car has had a lot of repairs. That is the car that the girl was driving on the highway.
- The school at the end of the road is the one he attends.
| Rule #1 A specific identity isn’t known | a, an | (no article) |
| Rule #2 A specific identity is known | the | the |
| Rule #3 When referring to all things or things in general | (no article) | (no article) |
Plural and Singular Nouns
Since the definite article precedes a noun to make it possess more of an exceptional nature, it is also used before plural nouns. These may have to be specific in any phrase or sentence.
- The pages of the book had withered away over time.
- The dresses in the shop were too gaudy for my taste.
- As Mary entered the kitchen, she dropped the plates, which landed on the floor with a crashing sound.
Where to use the Definite Article
Here’s where to use the definite article in English.
- Continents and Countries – In case a country or a continent comprises different parts, a definite article is used—for example, the U.K. or the Bahamas.
- Meals – The definite article precedes the kinds of food specified and the meals, but not any food in general. It is possible to say “the carrots,” “the dinner,” “the milk,” etc.
- Not for Professions and Jobs – The definite article cannot indicate a profession, like “I want to be the vet.” Instead, “I want to be a vet” is better.
- Directions – The definite article comes before any directions, like the North, the South, etc.
- Physical Features – The definite article “the” is always used before the name of an ocean, a sea, or a dessert. E.g., the Sahara Dessert, the Mediterranean Ocean, the Amazon, etc.
- Names of Unique Objects – In case a distinct object, like a monument or any other, is named, the definite article is used. E.g., the Taj Mahal, the Bible, the Ark of the Covenant, etc.
- For Certain Uncountable Nouns – E.g., the oil, the bread, the honey, etc.
- Surnames – The definite article comes before surnames when a particular surname is referred to, like the Smiths.

Definite vs. indefinite article
Articles are distinct adjectives used to exemplify nouns. All articles refer to nouns, and they specify their quality of definiteness. There is only one definite article in English, but there are two indefinite articles. The definite article is “the,” already introduced. The indefinite articles are “a” and “an.”
Indefinite articles represent nouns coming after them, which are non-specific. Consequently, when “an elephant” is said, it implies any elephant and not a particular elephant.
The use of the word “the” can be confusing. Nonetheless, it is a single word that is used for a specific noun. In terms of the indefinite article, “a” and “an” are used for non-specific nouns.
The general rule of thumb for either of these is that “a” is used for nouns/words that sound like consonants, and consonants, like in:
- a man
- a horse
- a useful tool
The indefinite article “an” is used before vowels. “An” also precedes words that have a beginning letter that sounds like a vowel:
- an umbrella
- an ostrich
- an heir
Examples of the definite article
Here are some examples of definite articles used in sentences in English:
- The house on the hill was known as a haunted house.
- The plane landed near the airstrip, missing the runway by a few yards.
- The most beautiful building on the street is the one made by a famous architect.
- The meal was lovely. I hear that they serve it a lot in the east of Asia.
- Do you know about the teenager who went trekking around the world in a month?
- The Atlantic Ocean is a vast waterbody with the best species of fish.
- The bread was baked to perfection by the chef who went to the Cordon Bleu Academy of Cookery.
Examples of the indefinite article
The indefinite article indicates nouns and words that are not explicitly referred to in speech and writing:
- She found a penny lying on the pavement across from her house.
- The road was empty, save for a single car parked near a tree.
- He dressed up soon. He was going as a spooky ghost to the Halloween party.
- Can I have an apple and a banana for breakfast?
- A monkey stole all the peanuts in the sack.
- We noticed a flock of birds above the houses.
- John is a one-man army against the opposing side.
- A university is located inside the town.
What is an article?
In English, an article is any word used to identify a noun or noun phrase.
Articles are “identifiers” of the nouns they come before. They are considered parts of speech in English. The word termed the “definite article” is “the.”
The words for the indefinite article are “a” and “an.” They combine with nouns and noun phrases to identify nouns. In English, articles have a characteristic purpose – to specify a noun’s identity. They give a definitive quality to the noun.
Articles in languages other than English define grammatical details about numbers, gender, case, etc.
In a broad sense, articles, the definite article, and the indefinite article are determiners. A definite article is an article giving a particular reference to a noun. The indefinite article refers to a noun in a general way.
“The” represents a certain noun (a specific object or a person, for instance). “A” or “an” represents any noun (any person or object in a general sense).
Definite article
- the (before a singular or plural noun)
Indefinite article
- a (before a singular noun beginning with a consonant sound)
- an (before a singular noun beginning with a vowel sound)
Count nouns
- Refers to things that can be counted and are either singular or plural form.
Non-count nouns
- Refers to things that are not counted and are always singular form.
Why are articles important?
Articles are essential parts of speech in English. They are modifiers appearing before noun phrases and nouns.
Sometimes known as adjectives, they aid in the clarification of the meaning of a noun in a phrase or a sentence.
When to use the definite article
The definite article’s use is before a noun. The purpose of the definite article is to refer to a singular or particular noun to give meaning to a phrase. This indicates the identity of the noun to the reader or the listener.
For instance, “The man who lives in the second house” specifies a remarkable man who lived in a particular house.
How to use the definite article
As mentioned earlier, definite articles have their position before a noun or are used in such a way as to refer to a specific noun in a phrase.
Used before singular and plural nouns, the definite article signals that a noun in question has a definite quality.
For example, look at the following:
- The cat that scratched me scurried off. (A certain cat)
- The Balinese people are friendly. (Referring to people belonging to a place)
- She lives in the Bahamas with her family. (Referring to a place)
- I was glad to see the lady that saved my child. (A certain lady)
- The water was too cold to swim in. (an uncountable noun)
- The French speak with a peculiar accent. (Referring to the people of France)
- The River Nile is long and treacherous. (Referring to the name of a river)
- The best food in the city is served at the restaurant. (Referring to the food – in a superlative sense)
FAQs
1. How many definite articles are there?
There is only a single definite article, and this is the word “the.”
2. Can you use the word “the” with any noun?
You can use the word “the” while referring to some nouns. You cannot use the word “the” before a person’s name.
3. Can you use the definite article with singular and plural words?
You can use the word “the” with singular and plural nouns. The word “the” is the definite article placed before the noun.
4. What are some examples of definite articles?
Here are some examples of definite articles:
- She climbed to the top of the mountain.
- Bob found himself alone in the classroom.
- The juice was tasty and fresh.
- I know the man who is the grocer.
References:
- Definite Article: Explanation and Examples (grammar-monster.com)
- Definite Article THE | Useful Rules & Examples in English – English Study Online
- What is a Definite Article? – Definite Article Examples – English Basics
- The definite article: ‘the’ | LearnEnglish (britishcouncil.org)
- What Is A Definite Article? | Thesaurus.com
- DEFINITE ARTICLE | English meaning – Cambridge Dictionary
- Articles: A Complete Grammar Guide | Grammarly
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



