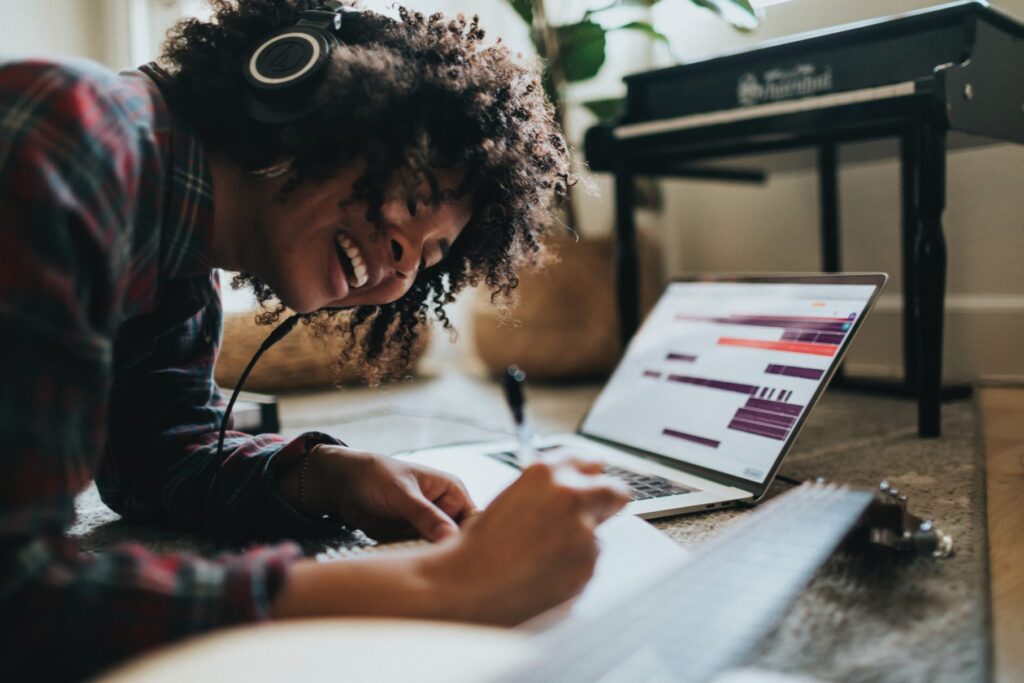
Conclusion transition words can be used by authors to reaffirm their arguments or ideas and wrap up an article, essay, or presentation. These words help writers to structure their ideas and guide the reader through the sentences. Conclusion transition words enable writers to indicate the completion of a paragraph and condense all the concepts that were discussed in the body of the article into a single concise statement.

Conclusion transition words for concluding paragraphs
These words indicate that the author is transitioning to the final paragraph of the article or essay. These can be used as introductions to closing paragraphs. Some conclusion transition words for concluding paragraphs include:
- To conclude
- In conclusion
- It can be concluded that
- When all is said and done
- To close
- In the long run
- In the final analysis
- Given these facts
- I will end by
Example sentences
- In conclusion, it can be said that this year’s budget will bring high economic development to the country.
- I will end by saying that this year’s carnival was a huge success.
- To wrap up, let us examine how this technology can be implemented in the market.
- Given these facts, the committee has decided to implement plan A for the next financial year.
- In the long run, the disease has proven to be too debilitating.
- From the analysis results, it can be concluded that the patient was losing too much blood.
- When all is said and done, the only thing that matters is that Jenna is happy.
Conclusion transition words for writing a summary
These words can be incorporated into a conclusion paragraph. However, they work especially well for succinctly bringing together a number of ideas. Some common words include:
- In summary
- To summarize
- In general
- In brief
- In any case
- All things considered
- In effect
- In essence
- In short
- In a word
- Generally speaking
- On the whole
- To sum up
Though these transition words can be used anywhere, “to summarize” and “in summary” are often used only at the ending,
Example sentences
- In brief, today’s presentation will briefly examine the advantages and disadvantages of the new product and the changes that can be made to improve it.
- Generally speaking, boys are more muscular than girls.
- We can conclude that the discovery of fire, on a whole, was the most significant development in human history.
- To summarize, one can argue that Shakespeare’s works continue to exert an impact on society at large.
- In short, it can be seen that this plan was a complete failure.
- In essence, his situation is not so different from hers.
Conclusion transition words for ending any paragraph
In some cases, before proceeding to a different topic, a writer may want to close a paragraph using conclusion transition words. It will bring the concepts in that paragraph to a close. Some common words include:
- For the most part
- With this in mind
- All in all
- This means that
- By and large
- Ultimately
These words could also serve as the introduction to a paragraph if it summarizes the earlier arguments.
Example sentences
- For the most part, the reception was a laid-back affair.
- All in all, the trip was really wonderful.
- This means that the company has to rethink its policies for the next fiscal year.
- We can say that, by and large, the student camp was extremely fruitful.
- Ultimately, it was his decision to end the marriage.
Restating ideas when concluding
Conclusion transition words are also helpful in rehashing a subject already discussed by the author. This is a popular speaking and writing technique because it calls attention to a point the author wants the reader or audience to remember. The following transition words can be used to wrap up or summarize by restating key points:
- As has been demonstrated
- As I have mentioned
- As stated above
- As has been noted
- As mentioned previously
- As we have seen
- As I have said
- As shown earlier
Based on which one is more appropriate, you can use either the passive or active voice for these words.
Example sentences
- As has been demonstrated, this technique can be successfully used in the resuscitation of patients in the emergency wards.
- As we have seen, the success of this program entirely depends on the market conditions.
- As mentioned previously, the company should try expanding its investment to other core sectors.
FAQs
Are conclusion and summary the same?
Since conclusion transition words are used for both summary and conclusion, it is necessary to understand the difference between the two.
A conclusion is generally used while ending an essay, speech, or article, combining all the arguments that were made in the body. But a summary can be written anywhere in an article. The summary can also be written in the introduction to let the readers know the topic that is about to be covered. The conclusion is more detailed than a summary, which provides a succinct rundown of the important ideas.
Are conclusion transition words necessary?
They are necessary to effectively conclude a document and to improve its readability.
Sources:
- K12reader – Conclusion Transition Words and Phrases
- ESL Forums – CONCLUSION Transition Words: Useful List & Examples
- Grammarly – All About Transition Words
- Smart Words – Transition Words
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



