What does “NVM” mean? When someone texts, “NVM,” what are they trying to communicate? The English language is changing thanks to the internet. Younger generations are using acronyms and abbreviations to save time and keystrokes when using common phrases.
Learn what “NVM” means in this guide…
“NVM” meaning and definition
“NVM” stands for “Never mind.” It is used as an acronym to explain to disregard something. For example, it could get used to disregard a task, action, or previous point of view. It is a common abbreviation used in online chat conversations, text messaging, and internet forums.
Never mind, the expression and phrase, is spelled with two words rather than one. The incorrect use of the phrase is “nevermind.”
Another way that someone could say “NVM” is by saying “NM.” Although, it is less common for a person to say, “NM.”
“NVM” is a type of initialism.
Capitalization
The acronym “NVM” is typically spelled in ALL CAPS or all lowercase letters.
Correct use: NVM
Correct use: nvm
Incorrect use: nVm
Incorrect use: nVM
Intention (synonyms)
Someone who uses “NVM” is trying to say the following:
- Disregard that
- Forget that
- Reverse that
- Don’t bother
Usage
“NVM” will get used in a variety of places, considering it is one of the more common abbreviations used in the digital world.
Social media: Snapchat, Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, and TikTok.
Chat rooms: Discord, internet forums, and more.
Text messaging: Group or direct text messages.
Formality
Typically, “NVM” will get used in informal conversations. For example, a conversation between two friends.
In formal settings, like while at work using Microsoft Teams or Slack, it’s best to avoid using “NVM.” Why? This acronym could potentially make a person sound unprofessional due to the way it’s most commonly used (informally).
History of “NVM”
The acronym “NVM” has gotten use since 2003, according to Urban Dictionary. Google Trends shows that the acronym has slowly gained in popularity and adoption since 2003. A core reason for the wide adoption of the acronym is that is looks somewhat similar to the word that it is describing.
For example, “nvm” looks similar to “never mind.” Making it far easier for others to understand and determine if they haven’t seen the acronym used prior.
Unusual uses of the term include showing annoyance to someone. For example, “NVM, you’ll never get it. LOL.” This example shows someone using the acronym to be rude and show superiority over another person.
Examples of “NVM” getting used in a conversation
Here are conversations where a person is using “NVM” in context:
Example one
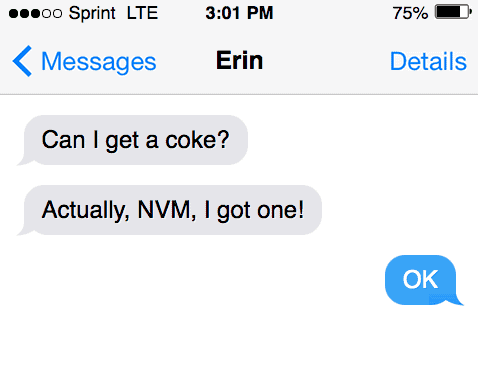
Friend 1: “I just got the store, do you need anything.”
Friend 2: “Yes, can I get a soda.”
Friend 2: “Actually, NVM!”
This example shows that the second friend is telling the first friend to forget the request. This could happen through online conversations and text message. The use of “NVM” is to disregard the first statement before it.
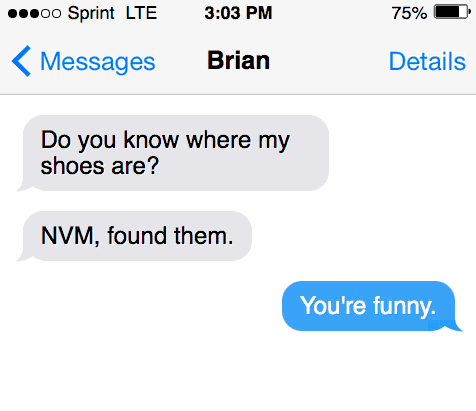
Example two
Friend 1: “I was talking to him for hours. And then I finally just decided, NVM, I’m going to move on here.”
Friend 2: “It’s really unfortunate that you have to forget about it. Oh well!”
Our second example shows a friend using “NVM” in the middle of a sentence. It is getting used as a way of posing an idea that the situation needs to be disregarded entirely. “NVM” can get used in the middle of sentences, alluding to “giving up” or “stopping.”
Similar short forms and abbreviations
Here are similar short form abbreviations that could get used in conversations:
FAI: Which stands for “Forget About It.” An acronym that infers asking someone to reverse an original request. Or to reverse the idea that was shared.
Sources
- Never Mind vs. Nevermind (vs. NVM and NM) – Merriam-Webster
- What Does ‘NVM’ Mean? | Acronyms by Dictionary.com
- What Does NVM Mean? – Cyber Definitions
- nvm – Urban Dictionary
- Nevermind – Wikipedia
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



