All of the sudden? All of a sudden? Which way is the correct way to say the phrase in American English? All of a sudden is a type of idiom that is used to describe the meaning, “suddenly.” It is used to place time or surprise into a statement.
An idiom is an adverb phrase. An adverb phrase modifies verbs in sentences. Since “all of the sudden” means “suddenly,” it often annoys readers when they are seeing this phrase used in sentences that didn’t happen suddenly.
Differences between “all of a sudden” and “all of the sudden”
All of a sudden is a popular idiom that is used in American English. It is used to describe something that took place unexpectedly or without warning.
The correct phrase to use is all of a sudden, rather than all of the sudden. There is no key difference between the two phrases. Rather, there has become an accepted format for how we used the idiom in the English language.
Both “all of the sudden” and “all of a sudden” are accepted. Although, when writing proper English (e.g., research papers, college- or university-level essays), it’s best to use “all of a sudden.”
To use the phrase correctly, it’s important to refer to a situation where the idiom modifies an adverb phrase. For example, a situation where, without warning, an occurrence took place. “All of a sudden” could simply get replaced with the adverb, “suddenly.”

Which phrase is grammatically correct?
There is no reason why “all of a sudden” is grammatically correct. The only grammatical reason for the phrase to be correct is that it is the most frequently used. Because of its wide adoption, “all of a sudden” has become the pinnacle for grammatically correct use.
Using “all of the sudden” is not considered a “big deal” when writing American English informally. Although, in formal settings, it’s better to use “all of a sudden.”
Note: The noun usage of “sudden” has mostly been abandoned by American English readers, writers, and speakers.
When to use “all of a sudden”
“All of a sudden” is the correct form of describing a situation, event, or occurrence that happened suddenly (adverb). When speaking American English, the proper way to say this phrase is with “all of a sudden” rather than “all of the sudden.”
Here are examples:
Example one: “All of a sudden, I was woken up from my bed. I heard a crash in the other room. And it made me scared.”
Example two: “It happened, all of a sudden. I couldn’t help it. It was like a wave of emotions was crashing over me.”
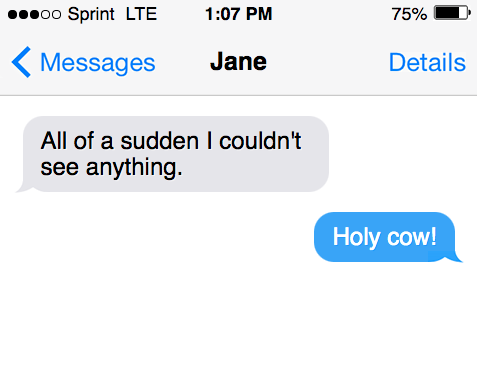
When to use “all of the sudden”
“All of the sudden” is a choice a writer could make when describing an event. Additionally, it could get used in conversation. If getting used in American English conversation, it is not considered “wrong.” It is simply a choice of how to use the idiom.
Here are examples:
Example one: “It happened all of the sudden. And I couldn’t stop it from occurring over and over.”
Example two: “All of the sudden I was faced with this extremely hard challenge in my life. And I couldn’t stop it from happening.”
Examples of use
While some readers and writers consider “all of the sudden” to be a “pet peeve” when used, there is no evidence that either one of the ways of using the phrase is more correct than the other.
Simply, a more adopted version of the phrase to describe the word “sudden.” Old English examples include the following, “Is it possible that love should of a sodain [sudden] take such hold?” (The Taming of a Shrew by William Shakespeare)

More sentence examples of “all of a sudden” getting used:
Example one: “All of a sudden, the football player decided that it was time to end the game. And began to run a very long touchdown winning pass.”
Example two: “It couldn’t have came together more quickly. All of a sudden we had the project finished before I could end the day.”
Remember, “all of a sudden” is just what American English speakers and writers refer to as an idiom. The correct phrase in English is “all of a sudden.”
Sources
- Idiom Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
- Idiom – Wikipedia
- Adverb Phrase Examples – YourDictionary
- Adverb phrases – English Grammar Today
- No Fear Shakespeare: The Taming of the Shrew: Act 1 Scene 1
- ‘All Of A Sudden’: Meaning & Context Of Phrase
- sodain – Wiktionary
- Meaning of suddenly in English – Cambridge Dictionary
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate