What’s the gist? What is a “gist?” A common idiom and phrase to hear in American English are “What’s the gist of it?” It’s a question that asks for a brief version of something long—a type of cheat sheet or terse version of something lengthy.
What does “gist” mean?
The noun “gist” means a “central idea; the essence.” Or rather, “the main or essential part of a matter.” In the phrase “the gist of a story,” we can see how the definition is used to ask for something shorter than the lengthy version.
The Collins English Dictionary says, “The gist of a speech, conversation, or piece of writing is its general meaning.” (singular noun)
The word Gist originates from Anglo-French, as in cest action gist en (reference). Or from Old French gésir (to lie or third-person sing). Or Latin jacēre (reference).

The gist noun or the central meaning of speech synonyms include:
- Burden
- Core
- Effect
- Essence
- Essential nature
- Bare bones
- Underlying reality
“Gist” in the legal manner
“Gist” can get used in a legal manner as well. For example, a “gist” is any legal action in the factor on which the action depends. A scenario where this can get applied is an alleged issue might be the gist of a legal indictment.
Another example of “gist” in the legal sense “The judge got the gist of the prosecutor’s argument when on the panel.”
In law, the essential point of an action consists of the meaning “gist.”
How is “gist” most commonly used
Most commonly, “gist” is used in the noun sense. Asking for the substance or essential nature of a text. Consider it the concentrated essence of a long test or speech.
For example, if a person is asking for the “gist” of an idea. They are looking for the critically important parts of the idea. The basic facts, the main point, and the core.
If a person asks for the “full gist,” it is simply a variation of the word “gist.” Where a person could ask for a longer version than the short version. Although not the entire version of a text.
What does “gist” mean in slang?
“Gist” in slang means the main point or part. Let’s presume it is two people engaging in a conversation. And the first person is telling a story. The length of the story extends far past the first person’s attention span.
In that scenario, the second person who is listening to the story could ask, “Can you tell me the gist of what happened? I don’t have the attention span for this.”
They are asking for the shortened version or the essence of the story.
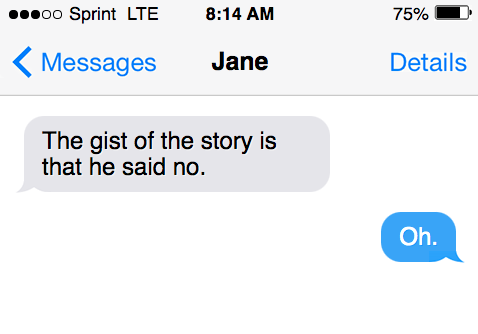
Examples of “gist” used in a sentence
- “I would love to hear the gist of what happened. I don’t have a lot of time right now to hear the full story.”
- “What’s the gist of the idea? I comprehend the whole picture. Although, I would love to learn what you feel the core concept can be.”
Common questions
Questions from those curious about the English language.
What does “gist” mean as a slang term?
The slang term for “gist” means to provide the shortened version or the essence.
What is a synonym for the word “gist?”
Synonyms for “gist” include essence, point, substance, burden, kernel, and import.
What is an antonym for the word “gist?”
Antonyms include the words meaningless, emptiness, irrelevance, unimportance, lack of meaning, and purposelessness.
Is it “jist” or “gist?”
The correct spelling is “gist,” and the incorrect spelling is “jist.” “Jist” is a variation of the word “gist” that can function as an adjective or adverb. More commonly used in the American South, the word “jist” is using a hard “j” pronunciation of the word “gist.”
It should not get used to replace the correct spelling “gist.”
Is “gist” a formal word?
“Gist” is a good word to use when asking for a summary or essential part of a story, concept, or idea. Asking for the “gist” of a concept is considered formal. It can get used in law, business, and general formal vocabulary.
What does it mean to have the “gist?”
It is a type of variation of the slang definition. The request for a shortened, essential, or bare-bones version of a text or speech. For example, “Can you give me the gist?” This sentence is a request for a short-form version of a lengthy text, concept, idea, or speech.
“Gist” can get used as part of a request or question. It is a message to the reader that a shortened version of the text is requested.

Sources
- Gist or Jist—Which is Correct? – Grammarly
- Gist Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
- Superjacent Definition & Meaning – Merriam-Webster
- jacere – Wiktionary
- English Translation of “gésir” | Collins French-English Dictionary
- gésir – Wiktionary
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



