What is a diphthong? How does a diphthong work? And how do I identify a diphthong in the English language? These are all great questions that you probably have. Diphthongs are known as gliding vowels, they have a unique purpose and definition in American English. To learn all about the diphthong, continue reading this comprehensive English guide.

What is a Diphthong?
Diphthongs are also known as gliding vowels. They are sounds that have two different vowels in the same syllable. That means you move your tongue and mouth position to produce two different sounds in a sequence when you pronounce a diphthong.
Diphthongs can be syllables that exist naturally and are heard as single vowels by the listeners. But they are also formed when two vowels merge due to rapid speech in conversation.
Definition
The word “Diphthong” is derived from the Ancient Greek word “Diphthongos,” meaning two sounds. It is a vowel where the sound changes clearly from one vowel sound to another within the same syllable.
| Diphthongs | Sound | Placement |
| “ai” “ay” | Long “a” | Middle of a word At the end |
| “ee” “ey” | Long “e” | Middle of a word At the end |
| “oa” “oe” | “Oh sound” | Middle of a word At the end |
| “oy” “oi” | Same sound | Middle of a word At the end |
How Does a Diphthong Work?
When we pronounce vowels, we usually hold our mouth and tongue in fixed positions. These are monophthongs, where a single vowel sound is produced while we let out one burst of air in a syllable. But diphthongs are produced differently from this general case. While pronouncing diphthongs, we move our tongue and parts of our mouth from one target position to another.
This means the sound gradually shifts from one vowel to a different one within the same syllable. But this is only noticeable under close inspection. We hear diphthongs as a single vowel like any other when we are not trying to look for them actively.
Diphthongs in Phonetic Alphabets
The phonetic alphabet is a system of notation used to signify the different sounds made while speaking in a language. In the International Phonetic Alphabet, single characters (usually Latin letters) represent a monophthong.
To represent diphthongs, two vowel symbols are used to identify the two sounds that occur together to form the diphthong.
Example
The pronunciation of the word “fun” is represented as “fʌn,” where the sound for the letter “u” is given by the symbol “ʌ.” This is a monophthong.
The word “loud” is represented as “laʊd,” where the vowel sound is represented as the combination of two symbols, “aʊ.” This is a diphthong.
Types of Diphthongs
There are several types of diphthongs based on how we classify them. Let us look at these types in detail, as they will help you understand what diphthongs are more clearly.
Change of Prominence of Vowels
The first way to classify diphthongs is to consider how the prominence of the vowel rises or falls while pronouncing the diphthongs.
If the pitch and volume of the vowel decrease while we pronounce the diphthong we call it a falling diphthong (for example- “eye”).
If the pitch and volume of the vowel rise when we pronounce the diphthong we call it a rising diphthong (for example- “new”).
Changing of Openness of Vowels
The vowels which we produce with a more open mouth are louder. We call them open vowels.
If the diphthong has a more open vowel at the end we call it an opening diphthong (for example- “new”).
If the diphthong has a more open vowel at the start we call it a closing diphthong (for example- “eye”).
If the vowels are closer in openness and the vowel moves from a more peripheral to a central position of the mouth, we call it a centering diphthong (for example- “ear”).
Distance Between Vowel Sounds
If we alter the mouth position significantly to reach from the first vowel sound to the next in a diphthong, we call it a wide diphthong (example- “found”).
If the mouth position does not change and we form the diphthong by gliding between two adjacent vowel sounds, then we call it a narrow diphthong (for example- “rain”).
Understanding The 8 Diphthong Sounds
There are eight distinct diphthong sounds in English. Each of them has its own representation in International Phonetic Alphabets.
Let’s look at them, along with some examples, and see what letters appear in words with these diphthongs.
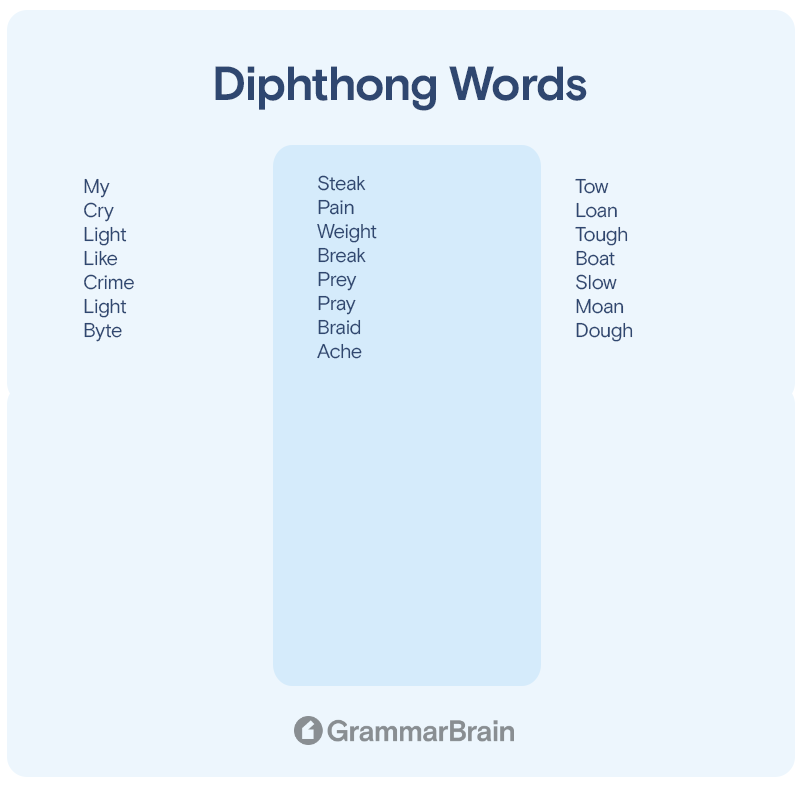
The phonetic symbol for the first diphthong is “ɑι.” It is usually used in words with the letters “i,” “igh” or “y.”
Examples
- My
- Cry
- Light
- Like
- Crime
- Light
- Byte
The phonetic symbol for the second diphthong is “eι.” It is usually used in words with the letters “ea,” “ey,” “ay,” “ai,” and “a.”
Examples
- Steak
- Pain
- Weight
- Break
- Prey
- Pray
- Braid
- Ache
The phonetic symbol for the third diphthong is “əʊ.” It is usually used in words with the letters “ow”, “oa” and “ough.”
Examples
- Tow
- Loan
- Tough
- Boat
- Slow
- Moan
- Dough
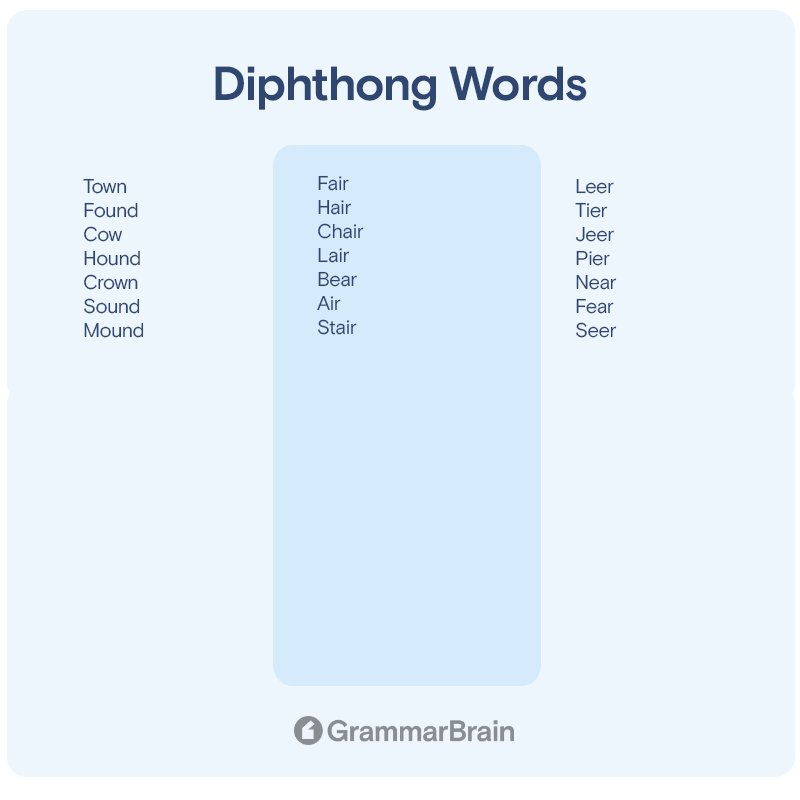
The phonetic symbol for the fourth diphthong is “ɑʊ”. It is usually used in words with the letters “ow” and “ou.”
Examples
- Town
- Found
- Cow
- Hound
- Crown
- Sound
- Mound
The phonetic symbol for the fifth diphthong is “eə.” It is usually used in words with the letters “ai” and “ea”
Examples
- Fair
- Hair
- Chair
- Lair
- Bear
- Air
- Stair
The phonetic symbol for the sixth diphthong is “ιə.” It is usually used in words with the letters “ee,” “ie” and “ea.”
Examples
- Leer
- Tier
- Jeer
- Pier
- Near
- Fear
- Seer
The phonetic symbol for the seventh diphthong is “ɔι.” It is usually used in words with the letters “oy” and “oi.”
Examples
- Oil
- Coy
- Foil
- Boy
- Soy
- Soil
- Boil
- Toil
The phonetic symbol for the eighth diphthong is “ʊə.” It is usually used in words with the letter “u.”
Examples
- Pure
- Lure
- Sure
- Cure
- Mule
Are Diphthongs Long Vowels?
Although diphthongs include two vowel sounds, they are not distinct vowels, we pronounce each vowel with a single exhalation.
When we pronounce two vowel sounds within a single syllable, the mouth parts and tongue have to move to accomplish it. It takes more time to do this than to keep the tongue and mouth position fixed while pronouncing a syllable.
This means, by definition, diphthongs are longer than most monophthongs. In other words, we can say that diphthongs are long vowels.
Why Are Diphthongs Important?
The diversity of the words we use impacts how well and distinctly we can express ourselves. To have a diverse group of words at our disposal we must be able to make many distinct sounds.
The more vowels we can produce, the more sounds we can pronounce. If we can combine monophthong vowels into diphthong vowels while we speak, it increases the richness of our stock of sounds. We can use the same vowels we can already produce to make new vowels which makes our language richer.
How to Identify a Diphthong
A diphthong is a vowel made by gliding from vowel sound to vowel sound. So by listening carefully, we can hear the two vowel sounds within the same syllable if it is a diphthong.
A way to identify diphthongs while pronouncing them is to notice if your tongue and mouth parts move during the production of the syllable. If it does move, then the vowel is a diphthong.
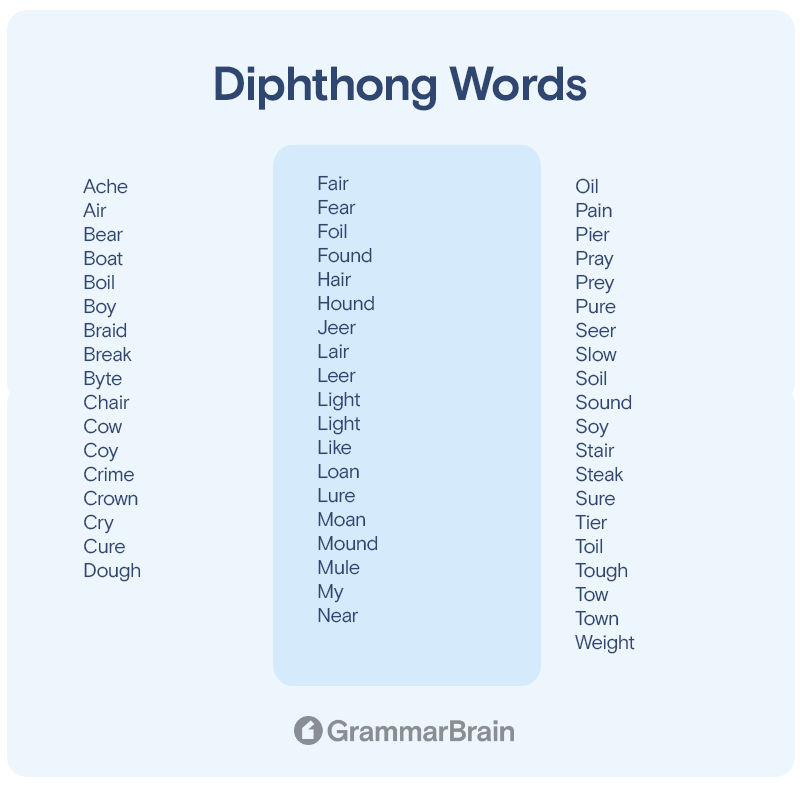
Examples of Diphthongs
Here is a list of some of the many words with diphthong vowels:
- Ache
- Air
- Bear
- Boat
- Boil
- Boy
- Braid
- Break
- Byte
- Chair
- Cow
- Coy
- Crime
- Crown
- Cry
- Cure
- Dough
- Fair
- Fear
- Foil
- Found
- Hair
- Hound
- Jeer
- Lair
- Leer
- Light
- Light
- Like
- Loan
- Lure
- Moan
- Mound
- Mule
- My
- Near
- Oil
- Pain
- Pier
- Pray
- Prey
- Pure
- Seer
- Slow
- Soil
- Sound
- Soy
- Stair
- Steak
- Sure
- Tier
- Toil
- Tough
- Tow
- Town
- Weight
Diphthong words list (images)
FAQs
How Many Diphthongs Are There In English?
There are eight distinct diphthong sounds in English. They can be of various types based on how we categorize them. These types include rising diphthong, falling diphthong, opening diphthong, closing diphthong, centering diphthong, wide diphthong, and narrow diphthong.
What Are The Eight Diphthongs Sounds With Examples?
The eight diphthong sounds with two examples each are as follows:
- ɑι – my, cry
- eι – steak, pain
- əʊ – tow, loan
- ɑʊ – town, found
- eə – fair, hair
- ιə – leer, tier
- ɔι – oil, coy
- ʊə – lure, pure
How To Pronounce A Diphthong
Pronouncing a diphthong requires moving the parts of the mouth and the tongue from the target vowel position to another within the same syllable. This is how we can change the vowel sound from one to another seamlessly within a single exhalation. How the vowels change depends on the specific diphthong we pronounce.
Do Diphthongs Exist In Other Languages
Yes, diphthongs exist in all languages. But the types of diphthongs used may vary from one language to another. All possible types of diphthongs are not present in each language. The exact list of diphthong sounds is unique to each language.
Is a gliding vowel a diphthong?
Yes, they are the same. Fun fact, ironically the word diphthong has no diphthongs.
Inside this article
Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.
Core lessons
Glossary
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Anecdote
- Antonym
- Active Sentence
- Adverb
- Adjective
- Allegory
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Ampersand
- Anastrophe
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Clause
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Consonance
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Determiner
- Declarative Sentence
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Diction
- Diphthong
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- False Dilemma Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Infinitive
- Indicative Mood
- Participle
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Prefix
- Predicate



